Weld-on hinges use smooth, entire leaves without any holes, which give them their name. They are made up of two leaves that come together in the center, much like all hinges. The two leaves come together to create a knuckle fastened by a pin. The linked leaves are held together by a pin put through their middles. Weld-on hinges do not have holes, unlike normal hinges containing two or more holes in each leaf. As they aren’t meant to be used with fasteners, they don’t need holes. Weld-on hinges, however, are intended to be fitted using welding. A welding torch can install a weld-on hinge to fuse each of its two leaves to the proper surfaces.
Weld-on hinges are a reliable, strong, and adaptable type of hinge. We provide a variety of hinges, such as bullet, heavy-duty, straight, double-pressed, and butt. Big duty weld-on hinges are great substitutes for more conventional hinges like butt and piano since they can support heavy loads and are acceptable for narrow frames.
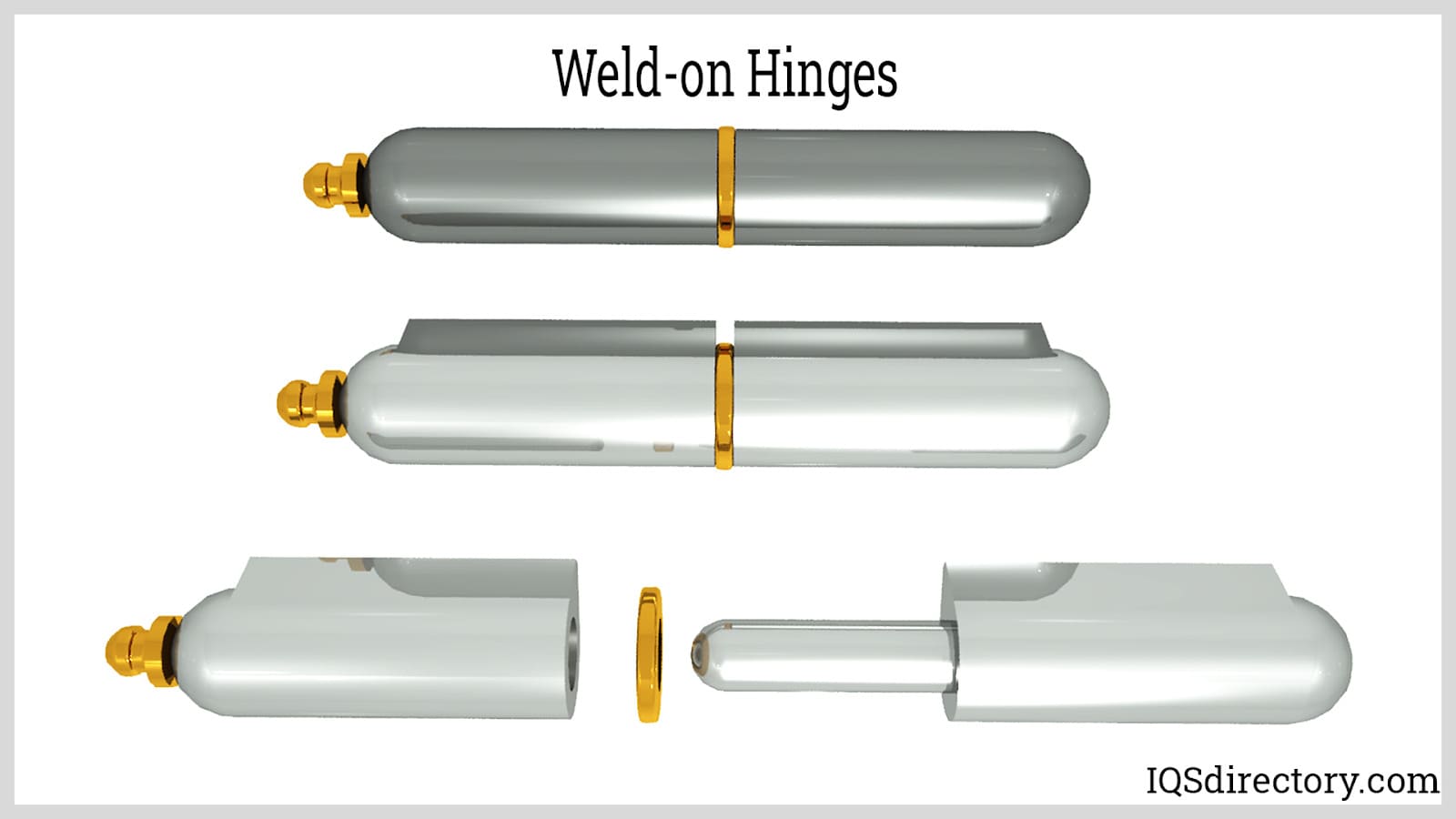

Materials used for Weld-on Hinges
- Iron, stainless steel, zinc-plated iron, low carbon steel, brass, steel, and aluminum alloys are typical materials used in weld-on hinges. The materials are drilled and cut to the precise shape of the hinge.
- Some weld-on hinges have grease nipples that make it simple to lubricate the hinge pin, making them the perfect solution for large doors.
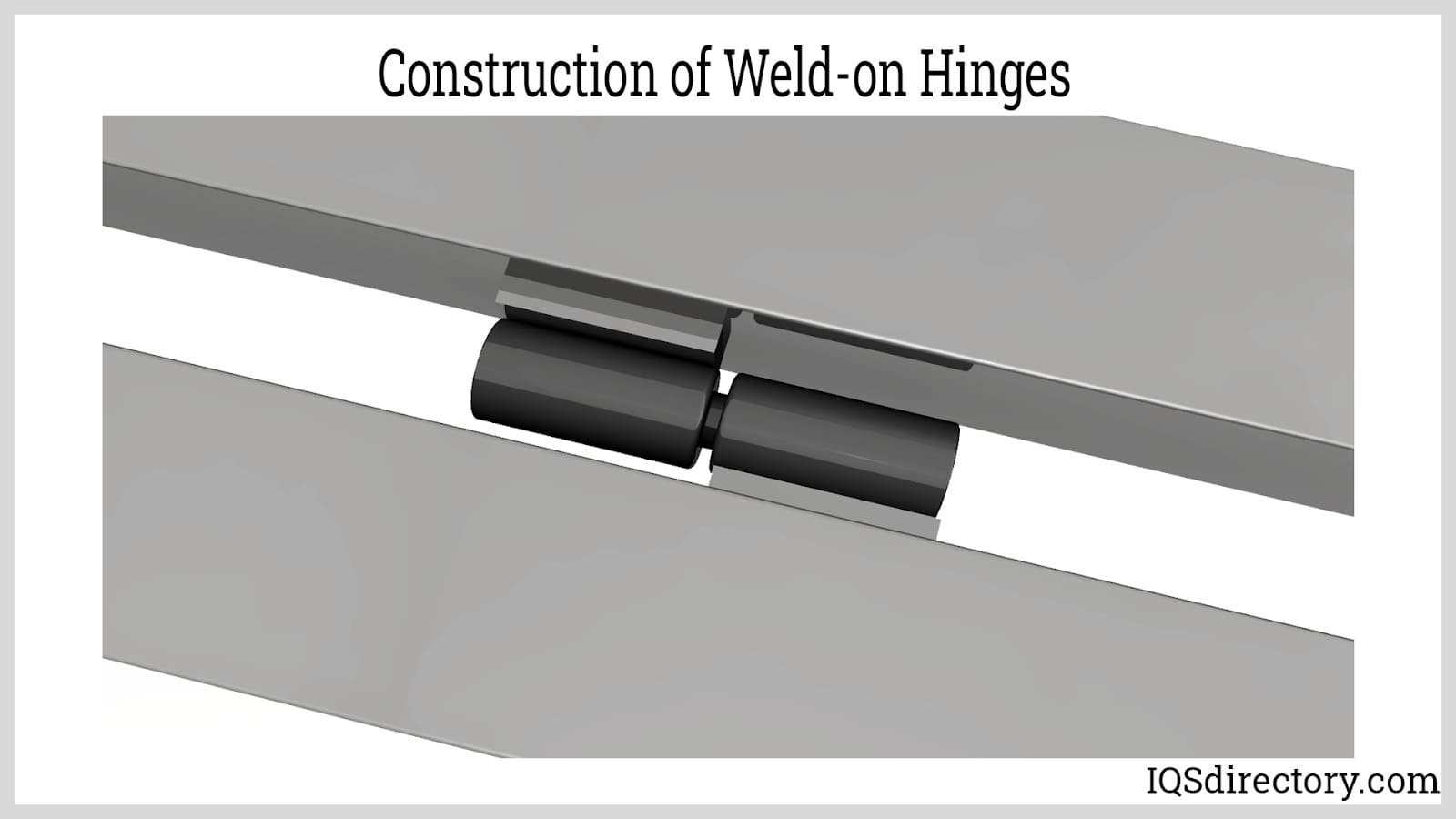
Construction of Weld-on Hinges
- Extrusion is the initial step in the procedure used to create weld-on hinges.
- In this procedure, a ram squeezes circular metal stock known as “billets” or “logs” through a die, a hollow profile that molds the metal as it is extruded into a particular form.
- Weld-on hinges consist of two independent hinge parts that may be directly welded onto surfaces.
- Weld-on hinges are also known as weld-on barrel hinges or plain barrel hinges since these portions are known as the male and female barrels.
- The barrel with the pin is the male barrel, while the barrel without a pin is the female barrel.
- In comparison, the male barrel is fastened to a structural surface, e.g., a door frame, and the female barrel is welded to the other surface, e.g., a door.
- The barrel without the pin should be placed on top because most lift-off doors often descend. As a result, the bottom barrels can support the door with exceptional load-bearing.
- For very heavy weights, heavy-duty weld-on hinges are an additional choice.
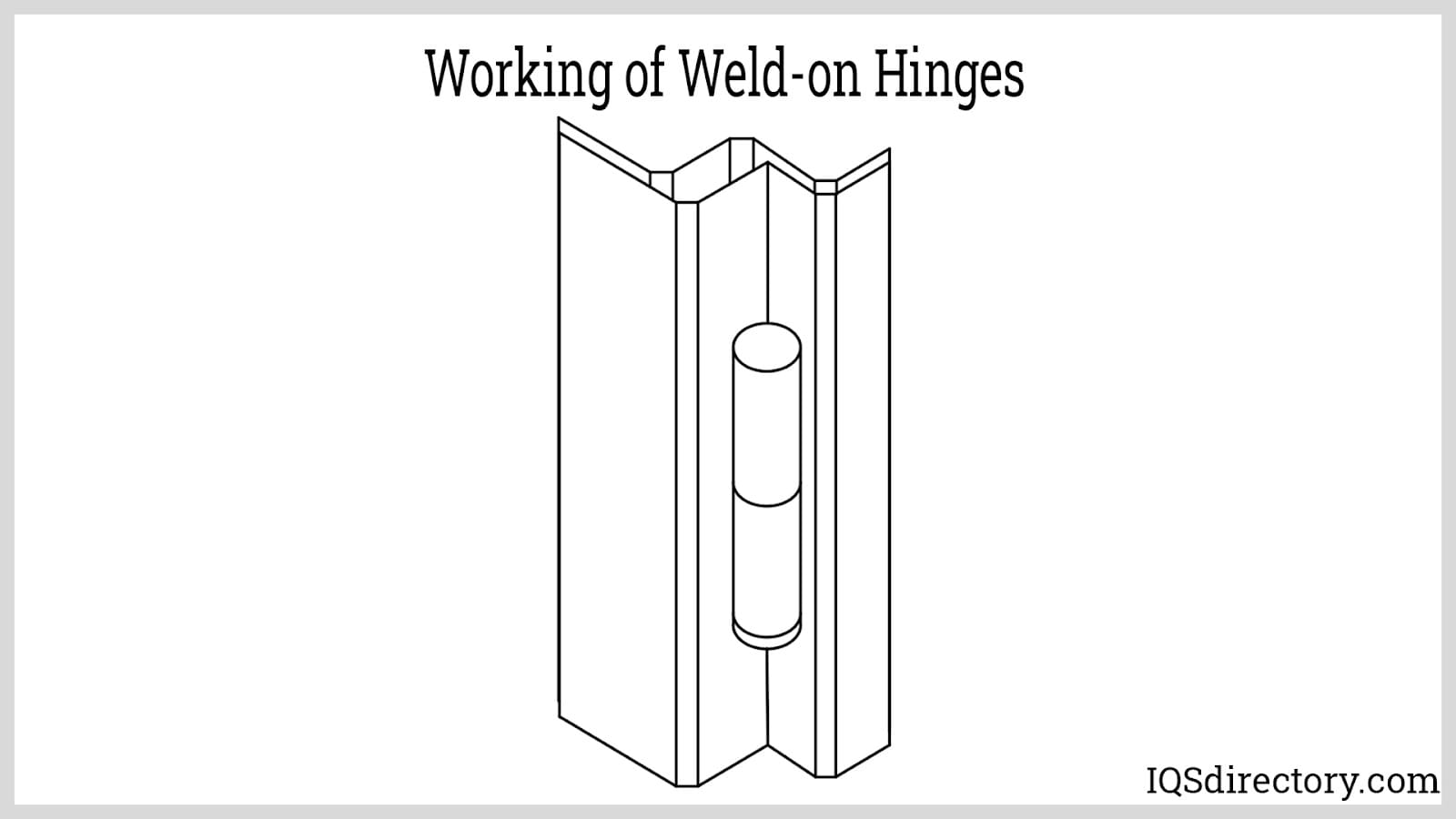
Working of Weld-on Hinges
Weld-on or bullet hinges have three essential components:
- The barrel side without a pin, sometimes referred to as the leaf side or female
- The pin-equipped barrel side, often known as male
- The bush, which straddles two divisions
- Male barrels are welded to structural surfaces, whereas female barrels are welded to the surface that needs to move.
- The female barrel needs to fit on top of the male barrel since doors with weld-on hinges are lift-off.
- This is because lift-off doors are frequently dropped. Therefore, the bottom barrel has to be more capable of bearing weight than the top.
- Lift-off doors can be easily removed from the hinges at any moment without the inconvenience of having to unscrew them.
- For added security, weld-on hinges can be fastened so that the gate or door can either be permanently installed or never be removed by taking it off.
Benefits of Weld-On Hinges
Weld-on heavy strength door hinges provide clients several advantages with notable characteristics, including:
- Pin made of precision-ground alloy steel
- Non-handed for mounting with either the right or left hand
- Dust sealing for harsh settings or outdoor use
- Greater flexibility than conventional hinges
- When utilized with certain things, weld-on hinges maintain the objects’ structural integrity. Pilot holes won’t need to be drilled into anything.
Applications of Weld-On Hinges
- Weld-on hinges are utilized when attaching one to another metal surface requires welding.
- They are perfect for various uses, including steel doors, gates, metal cabinets, containers, boats, and trailers.
- Large, mainly zinc doors, such as those on refrigerators and freezers, are frequently covered.
- Weld-on hinges are employed in industrial, commercial, maritime, automotive, shipping, building, and electronics sectors.
- Other things include BBQ pits, fishing gear, tool chests, cab enclosures, security gates, traffic signal controllers, truck or trailer bodies, boats, and cabs.
Choosing the Correct Weld-On Hinge Manufacturer
To ensure you have the most beneficial outcome when purchasing weld-on hinges from a weld-on hinge manufacturer, it is important to compare several companies using our directory of weld-on hinge manufacturers. Each weld-on hinge manufacturer has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each weld-on hinge company website using our patented website previewer to quickly learn what each business specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple weld-on hinge companies with the same form.


 Bolts
Bolts Fasteners
Fasteners Gas Spring
Gas Spring Handles
Handles Hinges
Hinges Latches
Latches Locks
Locks WIre Hooks
WIre Hooks Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services