Hinges are mechanical bearings used to join together two objects. They allow these objects to move on a limited angle of rotation relative to one another without falling apart. Read More…
We take our customer evaluations as our only measure of success. If our customers are not happy, we are not happy! We will work with you until we find the right hinges solution for you.

We are here to provide you with any hinge you could ever possibly need! We are the hinge specialists committed to bringing you a level of customer service that is unmatched by the competition.

Hardware Mfg. supplies stock inventory parts in addition to creating custom components for OEM and resellers. We work with a number of different industries such as agriculture, drug tablet, livestock, truck equipment, conveyors, and more.

We are Northeast Hinge Distributors, a dedicated supplier of high-quality hinges engineered to meet the performance, durability, and aesthetic requirements of modern manufacturing and construction. We work closely with OEMs, fabricators, contractors, and maintenance teams to provide hinge solutions that integrate seamlessly into doors, enclosures, cabinets, access panels, and industrial equipment.

At SELECT Hinges, we have been manufacturing high-quality hinges since 1989. We produce continuous-geared aluminum hinges as well as continuous pin and barrel hinges for doors that are subject to constant traffic. Our hinges are designed to withstand frequent use and have been tested for over 25 million cycles. Models are available for new construction or use on existing doors.

More Hinge Manufacturers
Applications
Hinges are indispensable mechanical devices that serve as a pivotal connection point between two solid objects, allowing for controlled rotational movement. Their engineering versatility and reliability make hinges essential components across an extensive array of industries and applications. In the realms of building construction and furniture manufacturing, hinges are commonly found in cabinet doors, entry doors, window frames, tables, and even specialized architectural features like folding partitions and adjustable shelving. Cabinet hinges facilitate seamless opening and closing, enabling ergonomic access and contributing to the longevity of furniture pieces, while door hinges provide the robust support necessary for high-traffic entryways in both residential and commercial settings. Window hinges not only enable smooth operation but also secure locking, which enhances energy efficiency and home security. In contemporary furniture design, specialized hinges enable foldable, space-saving, and adjustable pieces—key for urban and modular living environments, enhancing versatility, practicality, and user convenience.
In the aerospace industry, precision-engineered aircraft hinges are critical for the safe operation of control surfaces such as flaps, ailerons, and landing gear doors. These aviation-specific hinges are meticulously designed to withstand extreme pressures, temperature fluctuations, and vibrations, ensuring flight safety and performance. Similarly, in marine applications, corrosion-resistant marine-grade hinges are used for watertight doors, hatches, access panels, and lockers, providing dependable movement and security in harsh saltwater environments. Military and defense industries rely on heavy-duty hinges for armored vehicles, tank hatches, personnel doors, and secure access panels, demanding exceptional robustness and reliability under battlefield conditions and high-stress scenarios.
Turning our attention to the world of jewelry manufacturing and luxury accessories, delicate miniature hinges are fundamental in crafting lockets, watch cases, and ornamental boxes. These precision micro-hinges combine aesthetics with function, enabling smooth opening and secure closure for treasured keepsakes. In musical instrument fabrication, pianos and organs depend on specialized hinges for lids, action mechanisms, and key covers, where smooth, silent, and precise movement is paramount for both performance and aesthetic appeal.
Hinges also underpin security and access control in cages and fencing systems, where robust gate hinges and door hinges provide secure, smooth operation for both pedestrian and vehicular entry points. In home appliances and consumer electronics, innovative hinge designs enable the foldable and adjustable functionality seen in laptops, tablets, smartphones, and portable devices, striking a balance between durability, flexibility, and compactness. For example, laptop screen hinges are engineered to withstand thousands of open-close cycles while maintaining optimal torque and stability.
Within material handling and storage solutions, hinges play a crucial role in industrial cabinets, toolboxes, lockers, and enclosures. Here, hinges must withstand high usage frequency, support heavy doors or lids, and provide secure closure to protect valuable equipment or sensitive materials. The automotive industry relies on high-performance hinges for car doors, hoods, trunk lids, glove compartments, and foldable seats, all subjected to rigorous testing for safety, durability, and longevity.
For barrier and fencing applications, hinges enable gates and access points to swing open and closed, ensuring controlled, reliable ingress and egress in both residential and commercial settings. In modern architecture, innovative hinge systems support large pivoting doors, folding walls, and adjustable louvers, facilitating dynamic, adaptable spaces that enhance both the functionality and aesthetics of buildings. These architectural hinges are often chosen for their sleek appearance, concealed installation options, and smooth operation, supporting the latest trends in open-plan living and flexible workspace design.
From aerospace engineering to medical equipment and from public infrastructure to bespoke furniture, hinges provide the critical combination of movement, adjustability, security, and structural support needed to empower modern design and everyday convenience. Their versatility and adaptability ensure that hinges remain a core component in the advancement of technology, safety, and design innovation across all sectors.
Looking for the right hinge for your application?
- What are the most durable hinge materials for outdoor or marine use?
- How can you select the best hinge type for heavy-duty industrial doors?
- Which hinge designs are recommended for high-traffic commercial entrances?
- What are the benefits of concealed versus exposed hinges in modern furniture?
The History of Hinges
Hinges are among humanity’s most enduring mechanical inventions, with their roots tracing back thousands of years. The earliest hinge artifacts have been discovered in the ancient Middle East, notably at Hattusa, the capital of the Hittite Empire, dating as far back as 1600 BC. These early metal hinges were reserved for significant public works and sacred sites, symbolizing both technological advancement and societal importance. Ancient texts, including the Old Testament, reference hinges in the context of grand temples, highlighting their value and rarity due to the labor-intensive process of early metalworking.
As metalworking and blacksmithing advanced throughout the Middle Ages, hinges became more accessible and began to appear in the doors of common homes, wagons, and ships across Europe and Asia. The democratization of hinge production ushered in a new era of architectural innovation and personal property security, enabling the widespread use of doors, gates, and lockable chests.
The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries was a turning point in hinge manufacturing. The development of steam-powered machinery and precision metalworking tools allowed for mass production of hinges in increasingly complex forms. This era saw the introduction of the ball bearing hinge, patented by Stanley’s Bolt Manufactory in 1899, which offered smoother, quieter operation and longer service life. The result was a dramatic expansion in the use of hinges, from industrial machinery to mass-produced furniture and building hardware.
The 20th and 21st centuries have witnessed an explosion in hinge innovation, spurred by advances in materials science, automated manufacturing, and coating technologies. Modern hinges are now made from a diverse range of metals and high-performance plastics and can be treated with protective coatings for enhanced corrosion resistance and wear protection. Today’s hinges offer precise, customizable movement and are engineered for specialized applications in electronics, medical devices, aerospace, security systems, and more.
Want to learn more about hinge evolution?
- How did the industrial revolution change hinge manufacturing?
- What are the latest material innovations in hinge technology?
- How do modern hinges differ from their historical counterparts?
Design
Production Process
Modern hinge manufacturing is a sophisticated process that begins with careful material selection and precise engineering design. Manufacturers start by heating and preparing raw materials—typically metals such as steel, stainless steel, brass, bronze, or sometimes high-performance polymers—before shaping them using advanced machining techniques. These fabrication methods may include deformation, extrusion, casting, forging, or CNC machining. The choice of technique depends on the hinge’s intended application, required durability, production volume, and cost considerations.
After initial shaping, hinges undergo a series of secondary finishing processes to enhance performance and appearance. These may include electroplating for corrosion resistance, painting for aesthetics, galvanization for heavy-duty outdoor use, polishing for smooth operation, and rust-proofing for longevity in harsh environments. In many cases, hinges are also assembled with precision bearings or springs to augment their function, providing smoother or self-closing motion as required.
Materials
The choice of hinge material is critical, as it determines not only the hinge’s appearance but also its mechanical properties and suitability for specific environments. Common hinge materials include:
- Steel: Favored for strength and cost-effectiveness, often used in structural and industrial applications.
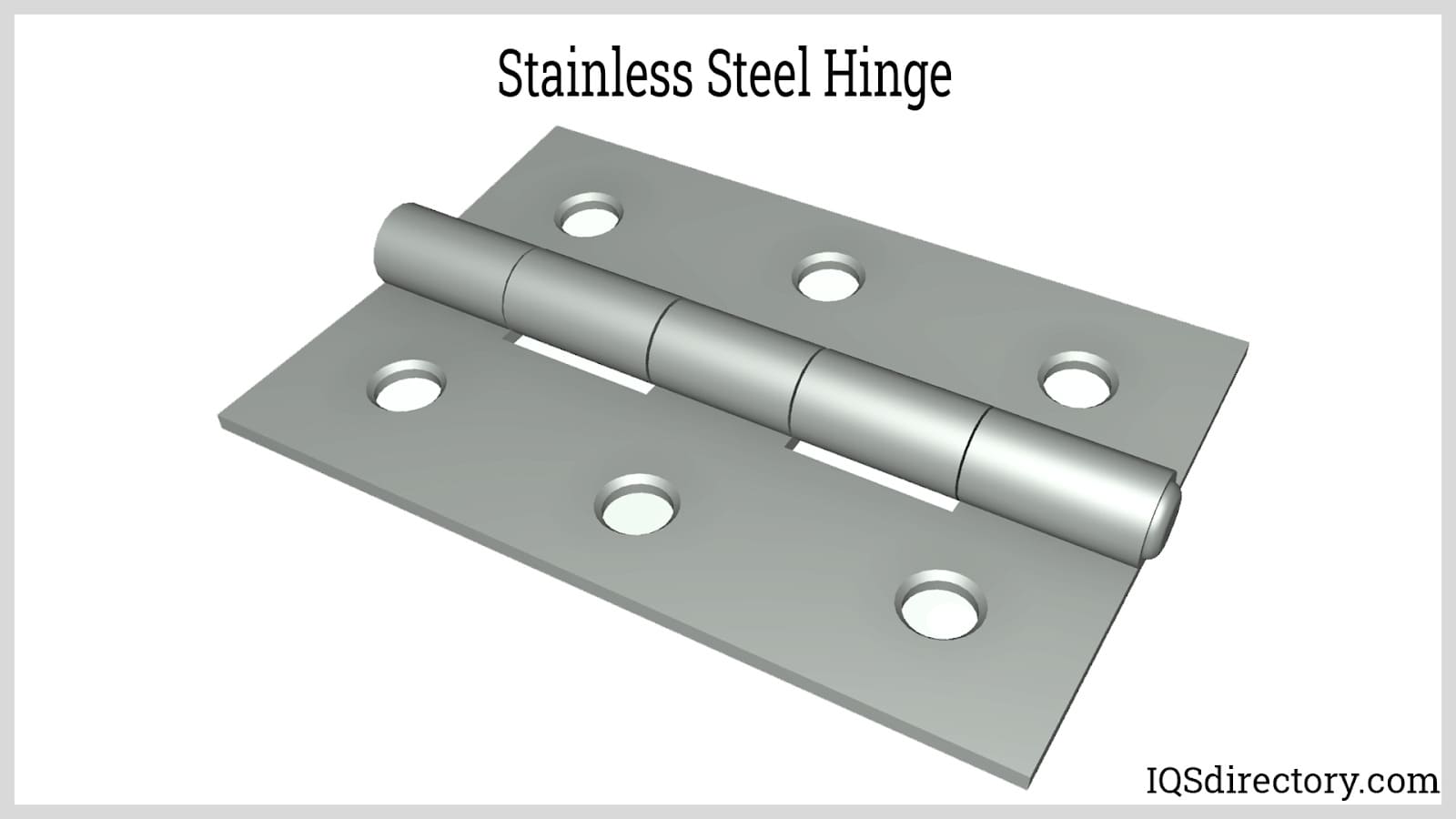
- Stainless Steel: Offers exceptional corrosion resistance, making it ideal for marine, outdoor, and medical settings.
- Brass and Bronze: Chosen for their decorative appeal and resistance to tarnishing, popular in high-end furniture and heritage restorations.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and inherently corrosion-resistant, used where weight savings are important.
- High-Performance Plastics: Such as nylon or Delrin, provide chemical resistance, electrical insulation, and a smooth, maintenance-free motion, commonly used in electronics and appliances.
Material selection is often guided by environmental factors (humidity, chemicals, UV exposure), load requirements, and specific industry regulations.
Considerations and Customization
Hinge design is a balance of engineering precision and creative flexibility. Manufacturers can customize hinge dimensions—including length, knuckle size, leaf thickness (gauge), width, pitch, and allowable end play—to suit any application. This flexibility allows for tailored solutions, whether the goal is to maximize strength for heavy gates, minimize visual impact for architectural features, or provide a unique finish for designer furniture.
Manufacturers can also offer custom finishes (polished, brushed, powder-coated, or anodized), specialized mounting options (concealed, surface-mount, or weld-on), and even integrated features such as dampers, springs, or electrical contacts for advanced functionality. The ability to match hinges to brand aesthetics and site-specific requirements is a significant factor when specifying hinges for commercial or high-end residential projects.
Need help with hinge selection or customization?
- What is the best hinge material for high-humidity environments?
- How can you specify a custom hinge for unique furniture designs?
- Which coatings provide the best protection against corrosion?
Types
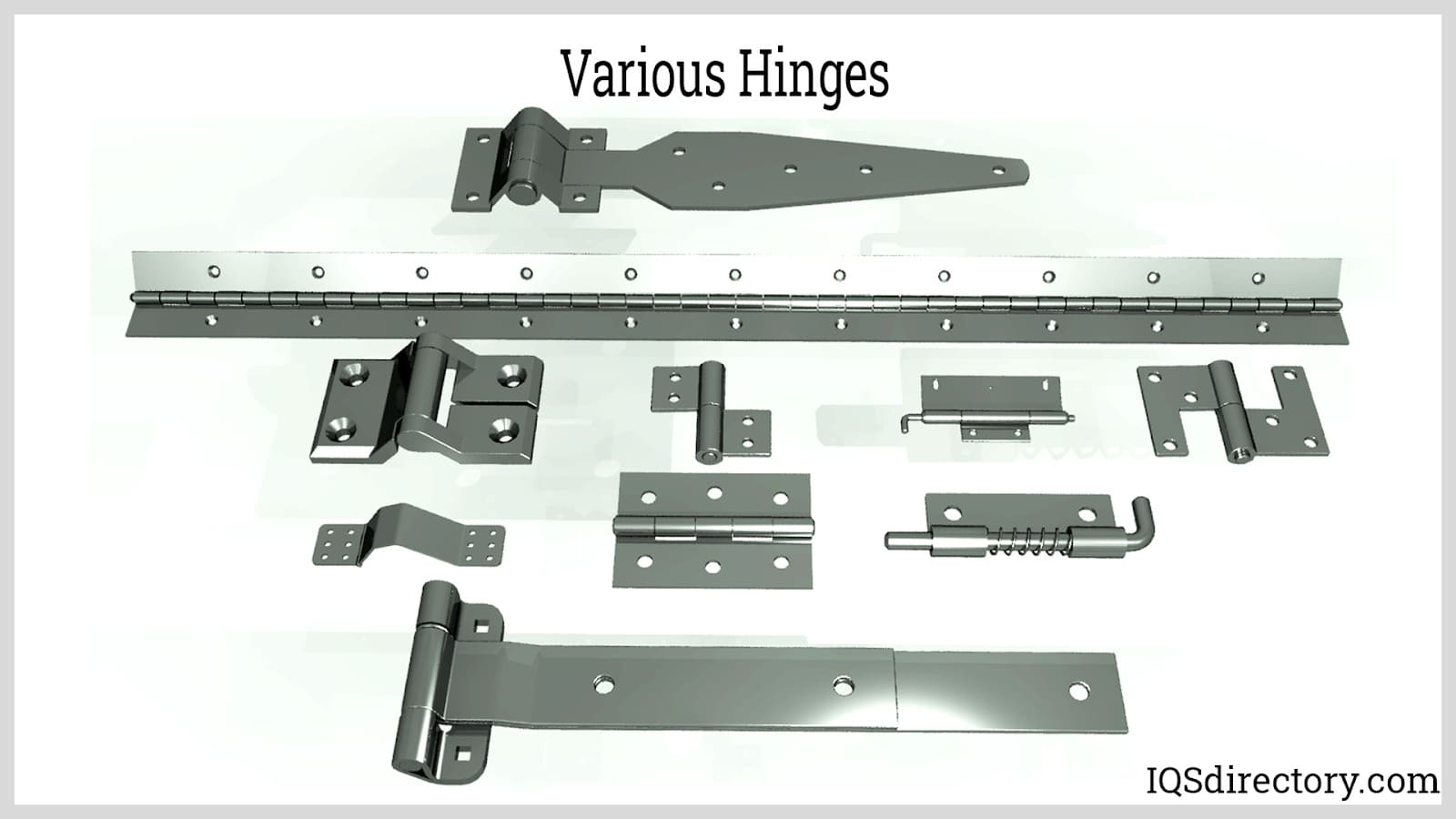
There is a remarkable diversity in hinge types, each engineered to meet the needs of specific applications and industries. Understanding the different varieties helps buyers and specifiers choose the most effective hinge for their requirements.
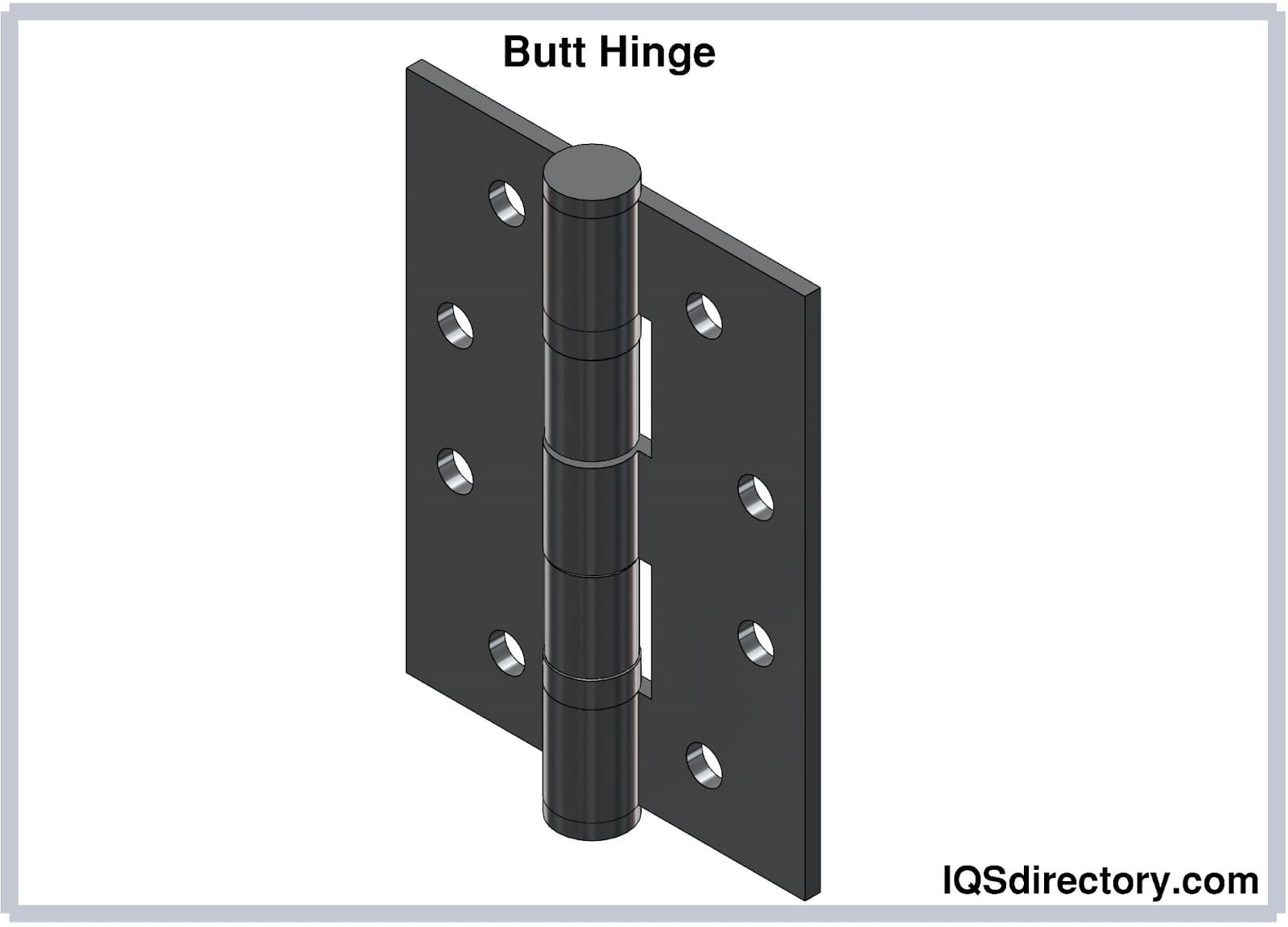
Butt Hinge
Butt hinges are the most widely used hinge type, featuring two identical leaves joined by a central pin. Commonly mortised into doors and frames, they provide smooth, strong support for entry doors, cabinetry, and utility enclosures. Variations include ball-bearing butt hinges for enhanced durability in high-traffic applications and security butt hinges with non-removable pins for added safety.
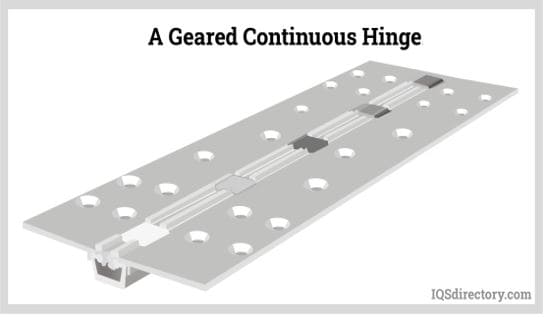
Continuous Hinge (Piano Hinge)
Continuous or piano hinges run the full length of a door or lid, distributing weight evenly and reducing stress points. They are ideal for long panels, toolboxes, pianos, and industrial enclosures. Some continuous hinges feature integrated springs or damping systems for specialized movement control.
Strap Hinge
Strap hinges are characterized by their elongated leaves, designed to provide extra support for wide or heavy gates, barn doors, and large chests. Their visually distinctive design is often used for decorative effect in rustic, heritage, or farmhouse architecture.
Pivot Hinge
Pivot hinges allow doors or panels to rotate around a central point at the top and bottom rather than along a side edge. This makes them ideal for heavy or wide doors in commercial, industrial, or contemporary architectural settings. Types include knife hinges, j-bolt pivots, and concealed/invisible pivots, each offering unique advantages for weight distribution and visual effect.
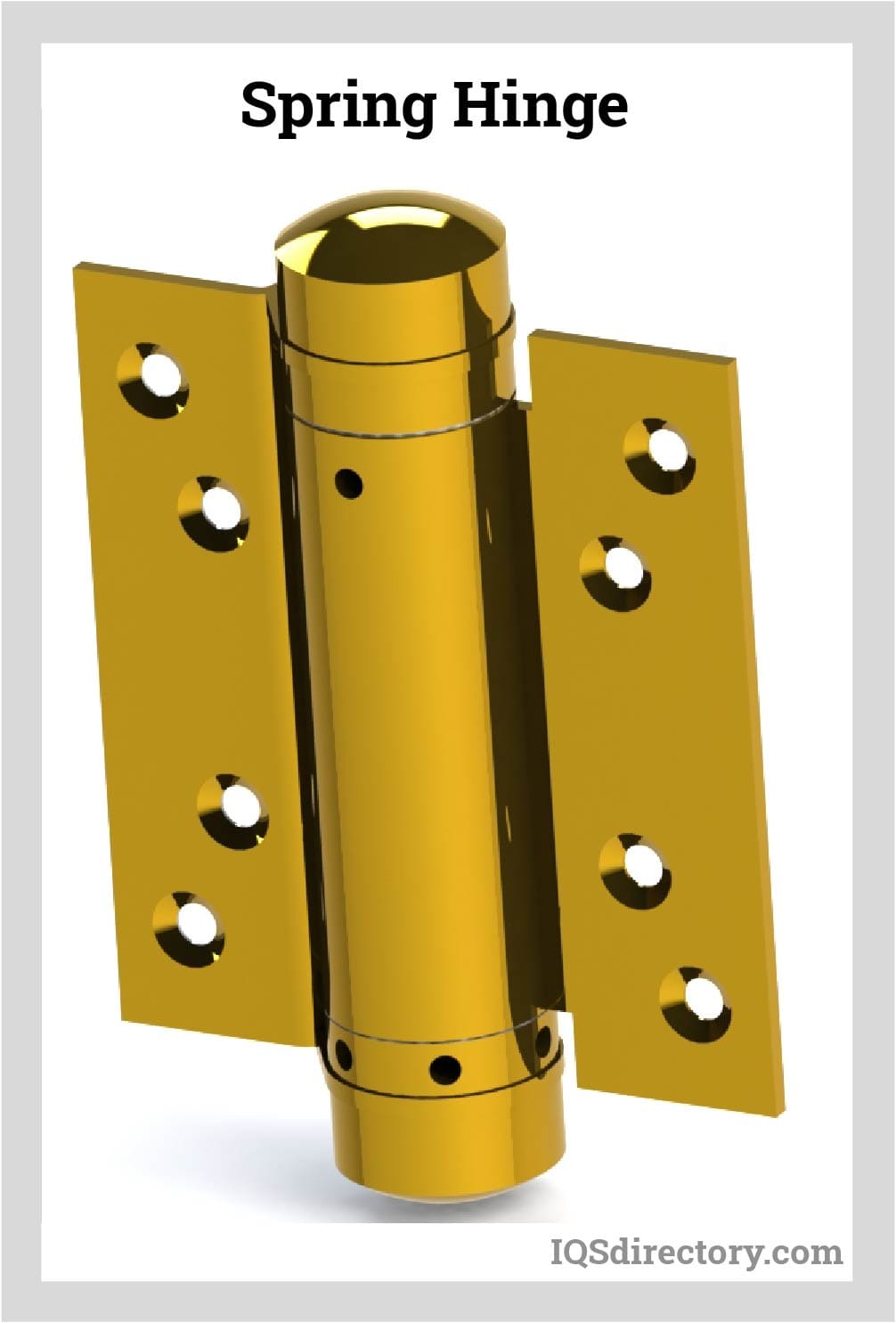
Spring Hinge
Spring hinges incorporate an internal coil or torsion spring, enabling self-closing or self-opening action. They are widely used for automatic door closing in fire-rated doors, security doors, and access panels where maintaining closure is critical for safety or energy efficiency.
Weld-On Hinge
Weld-on hinges are engineered for heavy-duty applications such as bank vaults, blast doors, and industrial gates. These hinges are welded directly to the mounting surfaces, providing superior strength and security. Lighter versions are used for wrought-iron gates and ornamental metalwork, often chosen for their long service life and tamper-resistance.
Heavy Duty Hinge
Heavy duty hinges are designed to carry substantial loads, often fabricated from thick-gauge stainless steel, bronze, or aluminum. Applications include industrial machinery, large gates, commercial doors, and specialty transport vehicles. These hinges are rigorously tested for load capacity, cycle life, and environmental durability.
Slip Joint Hinge (Loose Joint, Take-Apart Hinge)
Slip joint hinges allow for the quick removal of doors, panels, or lids, commonly used in electrical panels, livestock gates, fire truck compartments, and refuse containers. Their take-apart functionality is ideal for applications requiring regular access or maintenance.
Flag Hinge
Flag hinges are notable for their ability to rotate a full 360° around a fixed pin and for easy disassembly, making them suitable for removable doors, panels, or modular systems that require frequent reconfiguration.
Power Hinge (Electric Power Transfer Hinge)
Power hinges feature integrated electrical wiring, allowing for the seamless transfer of power or data across moving joints. These are often used in electronic access control doors, security systems, and smart building applications, ensuring both physical movement and electrical connectivity.
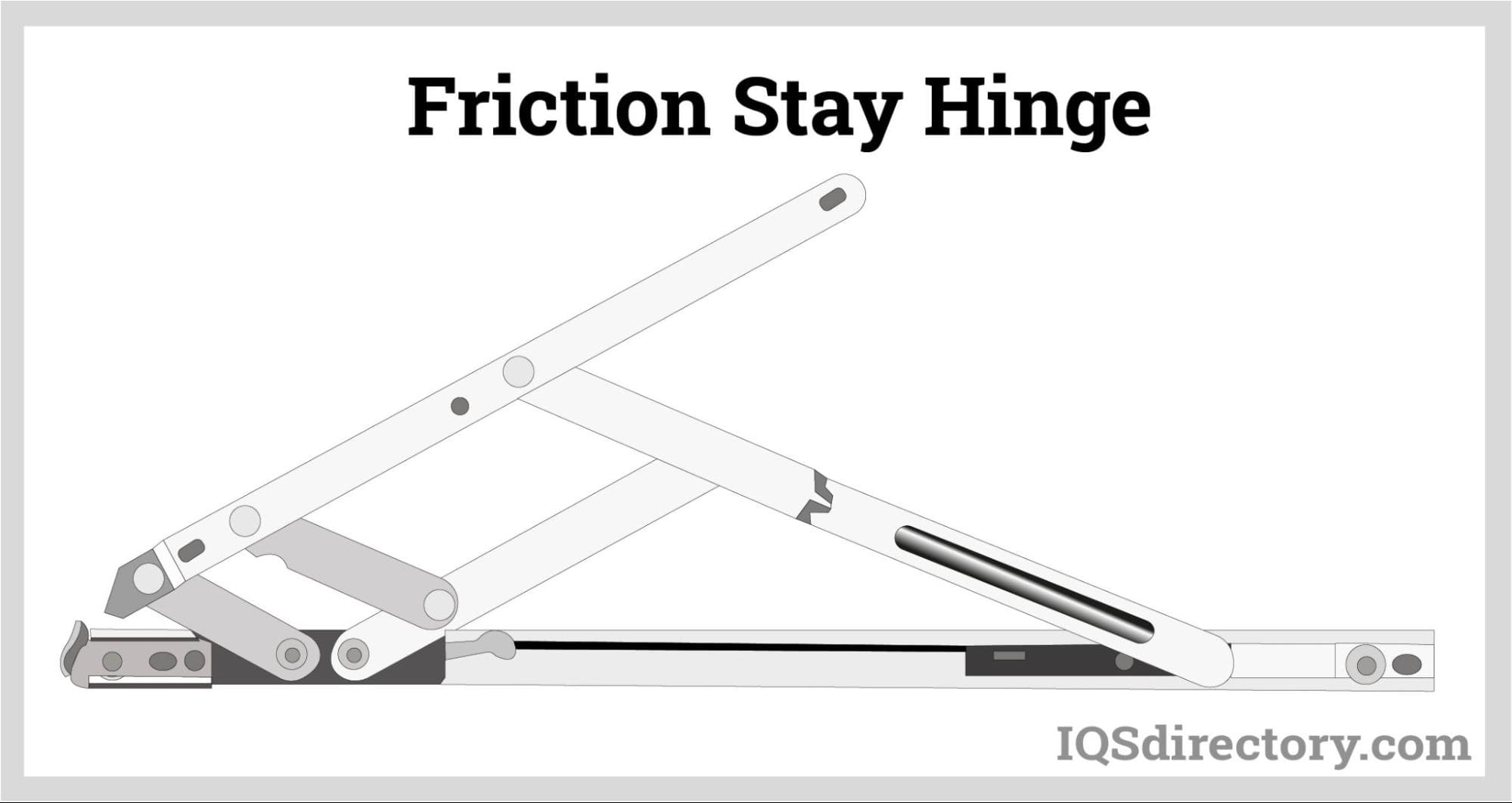
Friction Hinge
Friction hinges provide adjustable resistance, supporting lids, display panels, or laptop screens at any desired angle. With the growth of the electronics and portable device market, high-performance friction hinges are now critical for laptops, tablets, and industrial control panels where precise positioning is required.
Searching for the optimal hinge type?
- Which hinge type is best for high-security doors?
- How do continuous hinges benefit large industrial enclosures?
- What is the difference between spring and friction hinges?
Advantages of Hinges
When it comes to door and cabinet hardware, hinges offer several unique advantages over alternative mechanisms such as sliding tracks, magnets, or articulated joints. Their main benefits include:
- Stability and Durability: Hinges provide a solid, long-lasting connection that resists misalignment and mechanical failure, unlike sliding tracks that may jam or wear unevenly.
- Full Range of Motion: Hinges allow doors and windows to open completely for maximum accessibility and ventilation, which sliding systems may restrict.
- Security and Safety: Properly installed hinges are more difficult to tamper with or force open than magnets or cords, making them the preferred choice for high-security and safety-critical applications.
- Design Flexibility: Hinges can be customized for size, finish, concealment, or integrated functionality (such as damping or electrical transfer), supporting a wide range of architectural and design styles.
- Load-Bearing Capacity: Heavy-duty hinges are engineered to support massive weights, far exceeding the capabilities of most sliding or flexible joints.
- Maintenance and Longevity: With appropriate materials and coatings, hinges can provide decades of smooth, trouble-free operation, even under demanding conditions.
While alternative mechanisms like magnets or flexible joints may be suitable for lightweight or specialized applications, hinges remain the gold standard for most doors, gates, cabinets, and enclosures where reliability, security, and flexibility are paramount.
Accessories
A wide range of hinge accessories is available to enhance functionality, safety, and user experience. Choosing the right accessories ensures optimal performance, aesthetics, and longevity for your hinge installations:
- Tip-on Touch Latches: Allow handle-free operation of doors and cabinets, ideal for minimalist and modern designs.
- Angle Restriction Clips: Limit the opening angle of doors or gates to prevent damage to walls or nearby structures, especially useful in confined spaces.
- Doorstops: Prevent over-extension and potential damage; available in wall-mounted, floor-mounted, or integrated designs.
- Compact Adapters (Soft-Closing Mechanisms): Ensure smooth, quiet closure by controlling the closing speed and preventing slamming, widely used in kitchens and bathrooms.
- Stainless Steel Hinge Eye Bolts: Provide a secure, corrosion-resistant method for attaching hinges in marine, outdoor, or industrial environments.
- Door Cushions/Bumpers: Absorb impact and reduce noise, protecting both doors and adjacent surfaces in residential, hospitality, and office environments.
The decision to include hinge accessories should be based on application-specific requirements, such as desired aesthetics, space constraints, security needs, and environmental exposure.
Considering hinge accessories?
- What are the best hinge accessories for soft-close cabinets?
- How do tip-on latches contribute to modern kitchen design?
- Which marine hinge accessories are essential for corrosion resistance?
Installation
Proper hinge installation is critical for ensuring smooth operation, security, and long-term durability. The process involves:
- Marking and Alignment: Outline the hinge position on the door or frame, ensuring accurate alignment for smooth movement and even load distribution.
- Pilot Hole Drilling: Pre-drill screw holes to prevent splitting of wood or composite materials.
- Screw Attachment: Secure the hinge firmly using appropriate screws, ensuring the leaves sit flush with the mounting surface.
- Testing: Open and close the door or panel to check for proper alignment and smooth action; adjust as necessary.
- Even Distribution: For large or heavy doors, distribute multiple hinges evenly along the frame for optimal support.
- Optional Enhancements: Add soft-close adapters, tip-on latches, or other accessories to enhance functionality as required.
Always refer to the manufacturer’s installation guidelines and industry best practices, especially for specialty hinges or applications subject to regulatory standards.
Proper Care for Hinges
Regular hinge maintenance is essential for preserving smooth operation and maximizing service life, whether in domestic, commercial, or industrial settings. Key maintenance practices include:
- Cleaning: Wipe hinges with a damp cloth to remove dust, dirt, and grime. For tougher buildup, use a mild detergent or appropriate cleaning solution, ensuring no residue remains.
- Lubrication: Periodically apply a suitable lubricant (such as silicone spray or graphite powder) to moving parts, especially in high-use or outdoor environments. Remove the hinge pin if possible for thorough application.
- Screw Tightening: Check for loose screws and tighten as needed. For minor wear in screw holes, wood glue may offer a temporary fix, but consult the manufacturer for industrial-grade applications.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect for signs of corrosion, wear, or misalignment, particularly in environments subject to moisture, chemicals, or high loads. Replace damaged or worn hinges promptly to maintain safety and performance.
Need tips on hinge maintenance?
- How often should you lubricate exterior door hinges?
- What is the best way to clean stainless steel hinges?
- When should you replace rather than repair an old hinge?
Standards
Compliance with industry standards is a key factor in ensuring the safety, reliability, and interoperability of hinges in all applications. Major standards organizations include:
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI): Sets performance benchmarks for hinge materials, weight capacity, endurance, and safety through ANSI/BHMA standards.
- Builders Hardware Manufacturers Association (BHMA): Works with ANSI to develop and maintain standards for commercial and residential hardware, including hinges.
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Develops international standards to ensure global uniformity and compatibility in hinge design and manufacturing.
Adherence to these standards is crucial for manufacturers to avoid liability, product recalls, or reputational damage. For buyers and end-users, selecting hinges that meet or exceed ANSI, BHMA, or ISO standards ensures product quality, ease of replacement, and long-term reliability, while supporting international interoperability.
Non-compliance can result in safety risks, increased maintenance costs, and potential legal consequences. By prioritizing standardized products, both manufacturers and users benefit from enhanced safety, performance, and peace of mind.
Questions about hinge compliance or certification?
- What certifications should you look for in commercial door hinges?
- How do ANSI/BHMA standards ensure hinge safety?
- Are there specific standards for fire-rated or security hinges?
Things to Consider
When buying hinges, it’s important to evaluate several factors to ensure you select the right product for your specific needs:
- Intended Application: Consider whether the hinge will be used for doors, gates, cabinets, machinery, or specialty equipment.
- Load Requirements: Factor in the size, weight, and frequency of use for the attached object.
- Environmental Conditions: Assess exposure to moisture, chemicals, salt spray, temperature extremes, or UV light.
- Material and Finish: Choose a material and finish that offer the required strength, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal.
- Compliance: Ensure the hinge meets relevant industry standards and regulations for your application.
- Aesthetic Preferences: Decide on visible vs. concealed hinges, matching hardware finishes, and design style.
- Installation Simplicity: Consider ease of installation, availability of mounting hardware, and compatibility with existing systems.
- Additional Features: Determine if you need soft-closing, self-closing, security, or power transfer capabilities.
To find the best hinge solution, partner with a reputable hinge manufacturer or supplier that offers expertise, customization, and support tailored to your project. Our comprehensive directory connects you with industry leaders committed to quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction. Review their profiles, reach out to discuss your requirements, and choose a partner that aligns with your needs and budget.
Ready to start your hinge project?
- How do you request a custom hinge quote from manufacturers?
- What information should you provide when specifying industrial hinges?
- Where can you find reviews or case studies of hinge suppliers?
By considering all these factors and leveraging the resources of experienced hinge manufacturers, you can ensure a successful, long-lasting installation that meets your functional, aesthetic, and regulatory requirements. Explore our listings or contact us to connect with the right supplier for your next hinge project.
What are some common applications for hinges?
Hinges are commonly used in building construction, furniture manufacturing, aerospace, marine, jewelry design, musical instrument fabrication, security systems, home appliances, automotive, and architectural installations. They are found in doors, cabinets, gates, windows, pianos, industrial equipment, and more.
How did the industrial revolution change hinge manufacturing?
During the industrial revolution, the development of steam-powered machinery and precision tools allowed for mass production of hinges. This period saw the introduction of complex forms such as ball bearing hinges, making hinges more widely available and driving innovations in both residential and industrial hardware.
Which materials are commonly used to manufacture hinges?
Common materials for hinges include steel, stainless steel, brass, bronze, aluminum, and high-performance plastics like nylon or Delrin. The choice of material depends on strength, corrosion resistance, aesthetics, and the specific requirements of the application environment.
What are the main types of hinges and their uses?
Hinge types include butt hinges (for doors and cabinets), continuous or piano hinges (for panels and toolboxes), strap hinges (for gates and barn doors), pivot hinges (for heavy/wide doors), spring hinges (for self-closing doors), weld-on hinges (for heavy-duty gates), heavy duty hinges, slip joint hinges (take-apart), flag hinges, power hinges (with wiring), and friction hinges (for adjustable panels and electronics).
How should hinges be properly installed for best performance?
Proper installation involves marking and aligning the hinge, pre-drilling pilot holes, securely attaching with screws, and testing for smooth movement. For heavy doors, evenly distribute multiple hinges. Refer to manufacturer guidelines and consider necessary accessories for optimal performance.
What are the keys to hinge maintenance and care?
Maintain hinges by cleaning with a damp cloth, applying lubricant periodically, checking and tightening screws, and inspecting for corrosion or wear. Promptly replace damaged or worn hinges to maintain safety and performance, especially in high-use or harsh environments.
Which standards ensure hinge quality and safety?
Major standards for hinges include ANSI/BHMA (American National Standards Institute/Builders Hardware Manufacturers Association) and ISO (International Organization for Standardization). These standards cover material requirements, performance, endurance, and safety to ensure reliable products for all applications.
What should you consider when choosing hinges for your project?
Key considerations when choosing hinges include the intended application, load requirements, environmental conditions, material and finish, compliance with standards, aesthetic preferences, installation simplicity, and any desired features like soft-closing or security enhancements.




 Bolts
Bolts Fasteners
Fasteners Gas Spring
Gas Spring Handles
Handles Hinges
Hinges Latches
Latches Locks
Locks WIre Hooks
WIre Hooks Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services