Hinges are mechanical bearings used to join together two objects. They allow these objects to move on a limited angle of rotation relative to one another without falling apart. Read More…
We take our customer evaluations as our only measure of success. If our customers are not happy, we are not happy! We will work with you until we find the right hinges solution for you.

Jefco Mfg. has been a leader in the industry for over 40 years. With our experienced engineering and production team coupled with cutting edge technology, Jefco produces quality products for the Industrial, Marine, Aerospace, Defense, and Medical industries. We work closely with customers to meet/exceed their needs and design specs. Jefco has the ability to produce practically any design in any...
We are here to provide you with any hinge you could ever possibly need! We are the hinge specialists committed to bringing you a level of customer service that is unmatched by the competition.

Hardware Mfg. supplies stock inventory parts in addition to creating custom components for OEM and resellers. We work with a number of different industries such as agriculture, drug tablet, livestock, truck equipment, conveyors, and more.

Our company is the true hinges expert. We own over 50 patents for fasteners and we are completely ISO 9000 certified. Our products are made with the customer in mind, and we take your requests as requirements for service.
More Hinge Manufacturers
Applications
Hinges play a crucial role in a wide range of applications across various industries. Starting with building construction and furniture construction, hinges are extensively used in cabinets, doors, windows, and tables. Cabinet hinges provide smooth opening and closing of cabinet doors, while door hinges allow doors to swing open and closed with ease. Window hinges enable smooth operation and secure locking, contributing to energy efficiency. In furniture construction, hinges facilitate foldable designs and adjustable angles, enhancing functionality.
In the aerospace industry, hinges are employed in aircraft components like flaps, ailerons, and landing gear doors. These aviation hinges ensure precise control of moving parts, contributing to the safety and efficiency of aircraft during flight. Likewise, in marine applications, hinges are essential for various components like doors, hatches, and access panels, providing reliable and secure movement in harsh marine environments. Similarly, in military and defense applications, hinges are vital for military vehicle components like hatches, doors, and access panels. They provide robustness and reliability under harsh conditions, ensuring smooth functionality and quick access when needed.
Moving on to the jewelry and locket industry, miniature hinges are used to create delicate and ornamental lockets, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of the jewelry pieces while allowing them to open and reveal hidden elements or photographs. In the realm of musical instruments, meanwhile, pianos heavily rely on hinges for the complex action mechanism that allows the hammers to strike the strings with precision and generate various tones.
For cages and fences, hinges are crucial for gates and doors. Heavy-duty hinges are employed to support the weight of these structures while providing smooth opening and closing, ensuring security and ease of access. Home appliances and electronics, on the other hand, often incorporate hinges for foldable and adjustable parts. Laptops and smartphones, for instance, use hinges for the opening and closing of screens, offering flexibility and portability.
In material handling and storage, hinges are utilized in storage lockers, toolboxes, and industrial cabinets. These hinges endure frequent use and guarantee secure closure, making them integral to organizing and safeguarding items. In the automotive industry, hinges are simply essential for car doors, hoods, trunks, and foldable seats. These hinges undergo rigorous testing to ensure long-lasting performance and safety for passengers.
For barrier and fencing applications, hinges are indispensable for gates and access points. They allow gates to swing open and closed, providing controlled entry and exit to designated areas, whether for pedestrian or vehicular use. Finally, in architecture, hinges find use in various movable architectural elements, such as large pivoting doors, foldable walls, and adjustable louvers. These innovative hinge applications allow for dynamic and adaptable spaces, enhancing the functionality and aesthetics of modern buildings.
In conclusion, hinges are versatile and essential components utilized in numerous applications across a wide array of industries. Their role in providing smooth movement, adjustability, and structural integrity makes them indispensable for creating functional and practical designs in cabinets, doors, windows, gates, lockers, tables, airplanes, marine and military vehicles, jewelry, pianos, cages, fences, home appliances, electronics, and more. From aerospace to architecture, hinges continue to play a crucial role in enhancing various aspects of our daily lives and industries.
The History of Hinges
Hinges are among our oldest and most abiding companions. While no one can say when exactly they were invented, we do know that they’ve been in use in the Middle East since at least the Bronze Age. Some of the oldest hinge artifacts we have today were found in Turkey, where Hattusa, the ancient capital city of the Hittite Empire, once stood. Dating back to around 1600 BC, these hinges were likely installed only on important and/or sacred buildings. This usage seems to have held across the ancient world; in the Old Testament, hinges are mentioned just once, in reference to the temple of King Solomon. In addition, those hinges found in ancient Assyrian and Babylonian cities have only been found where temples once stood, not homes. We can assume this was because hinges were expensive to make.
By the time the Middle Ages arrived, blacksmithing was a more common profession and metal was less expensive. As a result, laypeople too began using hinges on their doors. Then, the use of hinges diversified; people began attaching hinges to items like gates, wagons, ships, jewelry boxes and lock boxes.
A few hundred years later, the Industrial Revolution kicked off, ushering in the advancement and production growth of hinges. This was largely in part due to the necessity of hinges on many of the new machines. It was also because of machines that hinges could suddenly be produced with more complexity, precision, speed and volume. One innovation of the time was the hinge featuring ball bearings, which allowed for smoother openings. The American company, Stanley’s Bolt Manufactory, which later became StanleyWorks, received a patent for this hinge design in 1899.
The 20th and 21st centuries have since brought many more innovations to hinge manufacturing, including: a wider range of materials with which to work, the ability to apply protective coatings, more complex design possibilities and faster production. In addition, modern hinges allow for a greater range of motion of the items to which they’re attached.
Design
Production Process
Hinge and latch manufacturers begin the production process by heating the metal material they will use. Once the metal is hot enough, they put it through machining processes such as: deformation, extrusion, casting and/or cutting. They base their machining choice on factors including: budget, required production volume, required production speed and design complexity.
Once they machine the hinge, manufacturers often put it through one or more series of secondary processes. If they do this, they do it to perfect the piece, and thus engage in processes such as: plating, painting, coating, polishing, rust-proofing, galvanization or smoothening. They decide which secondary processes, if any, to employ based on the frequency with which they will be exposed to damages like corrosion, wear or abrasion.
Materials
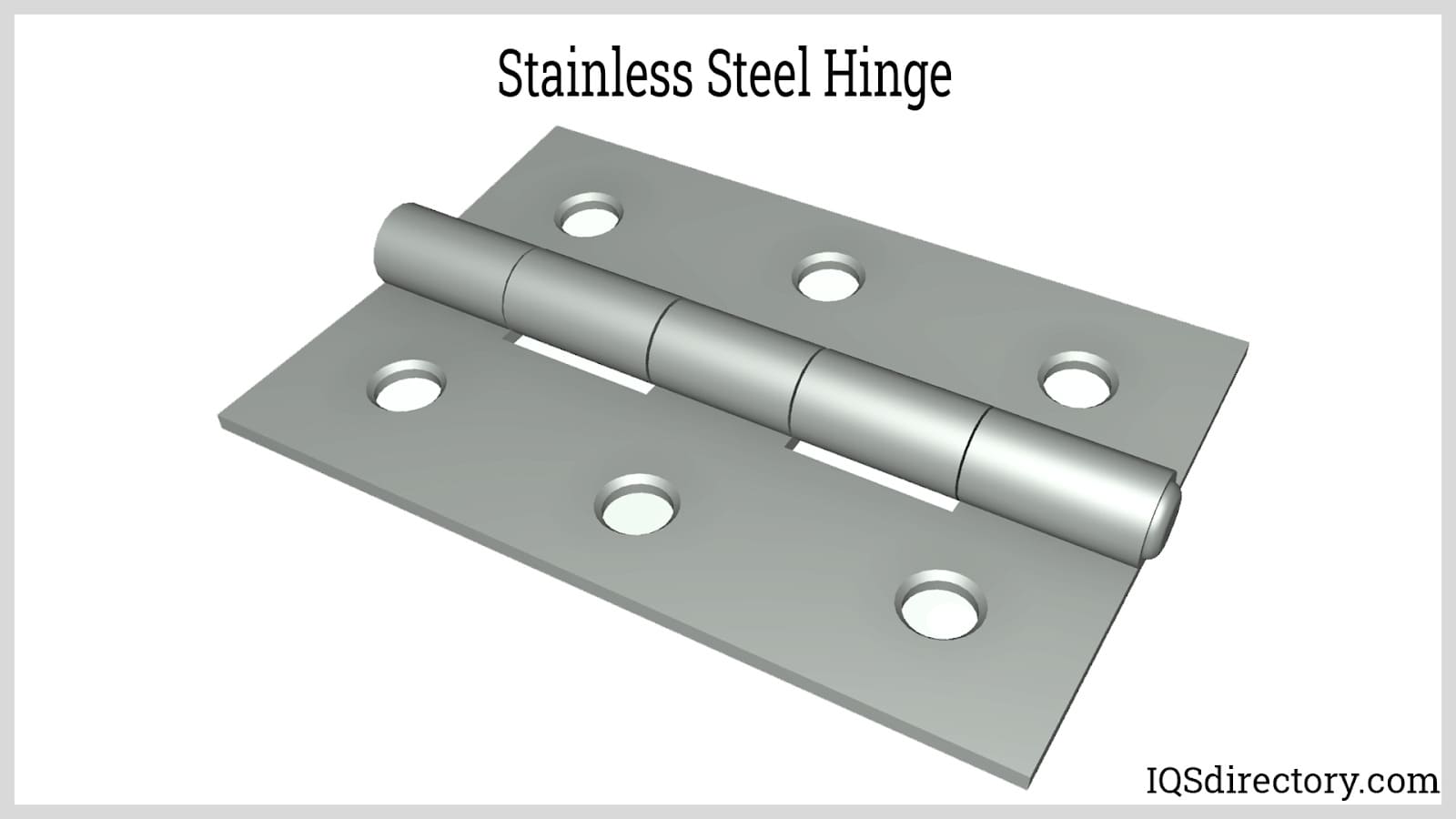
Most often, manufacturers make hinges from hollow or solid metal materials. Common examples include: steel, stainless steel, chrome, copper, nickel, solid brass and bronze. Each of these metals display different qualities related to: durability, tensile strength, corrosion resistance, ductility, temperature resistance, aesthetic appeal, etc. A brass hinge, for instance, is best as a decorative hinge because it has such a nice color. In addition, manufacturers sometimes use plastic hinge material. Plastic material creates inexpensive hinges that are heat, rust, chemical and UV resistant, and do not require lubrication.
Considerations and Customization
When designing, hinge manufacturers usually start with three basic elements: the leaves, the knuckle and the hinge pin. The leaves are plates that extend outward. They are held together by the knuckle, a hollow joint. In turn, the knuckle is held together by the pin. During installation, users attach the leaves to the separate surfaces they’d like to hold together and drill a hole in each leaf, so that they can fasten them.
Aside from these details, manufacturers have a lot of creative license. They vary them by: hinge length (measured parallel to the pin), hinge length (measured from leaf outer edge to outer edge), knuckle length (measured from the individual knuckle parallel to the pin), gauge (leaf mm thickness), leaf width (measured from center of pin to outer edge of leaf), slope (loose angular movement of leaves relative to pin), pitch (distance from one knuckle edge to the same edge of another knuckle on the same leaf) and end play (extent to which leaves move axially). In addition, manufacturers can deliberately create end play gaps, or spaces between the knuckles and between the leaves. End play gaps assist in increasing the motion and fluidity in the movement of the hinge.
There are a wide range of ways that they can customize your hinges. For instance, they can match most any custom hinge size request. They also can add embellishments like complementary or matched colors and shiny finishes. If you don’t want your hinge visible, manufacturers can even design it to be completely hidden.
Types
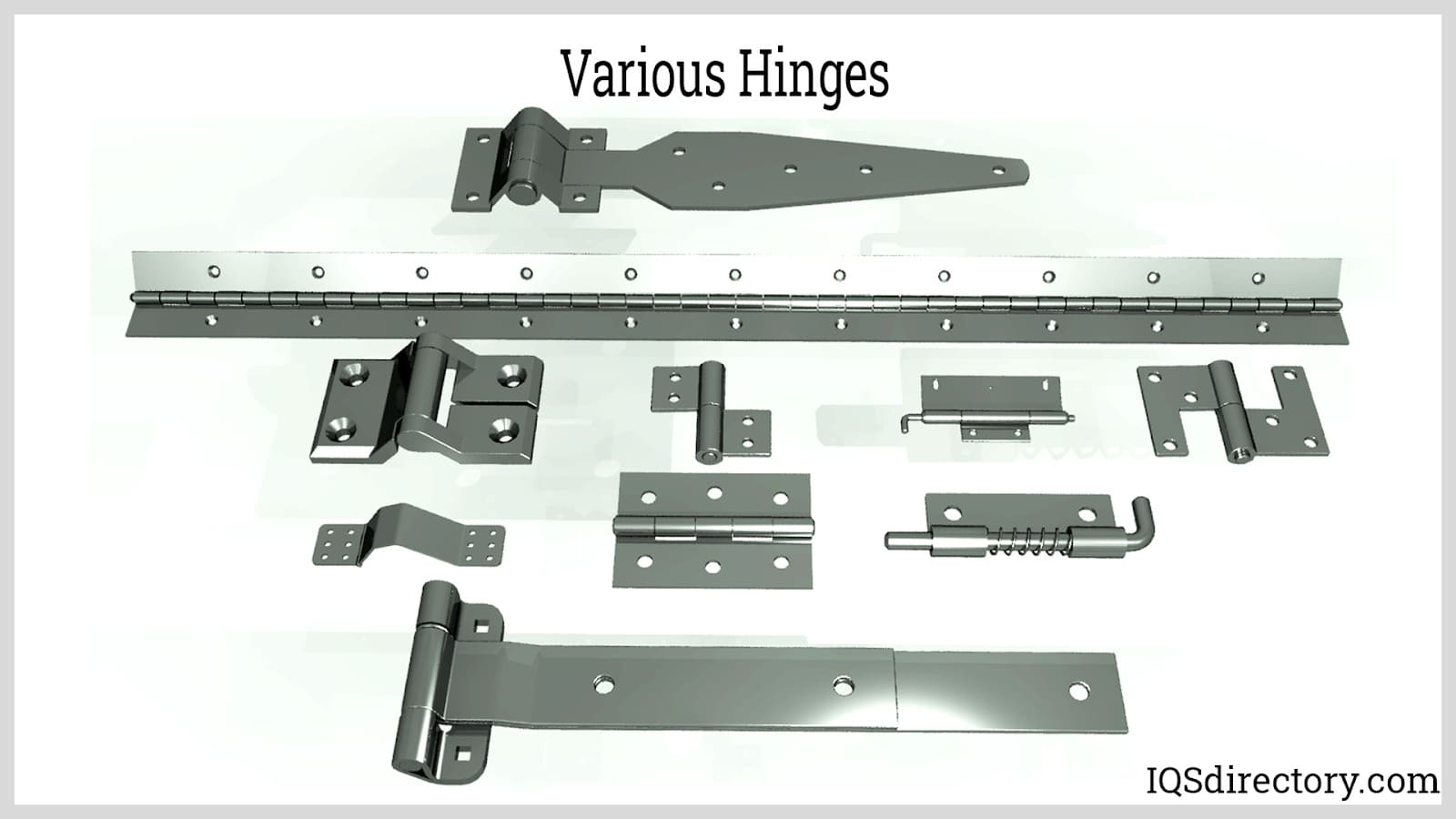
Hinges are manufactured in a wide variety of compositions and configurations, due to the overwhelming number of industries in which hinges are utilized. The most simplistic variety of hinges are butt hinges and continuous hinges, also known as piano hinges.
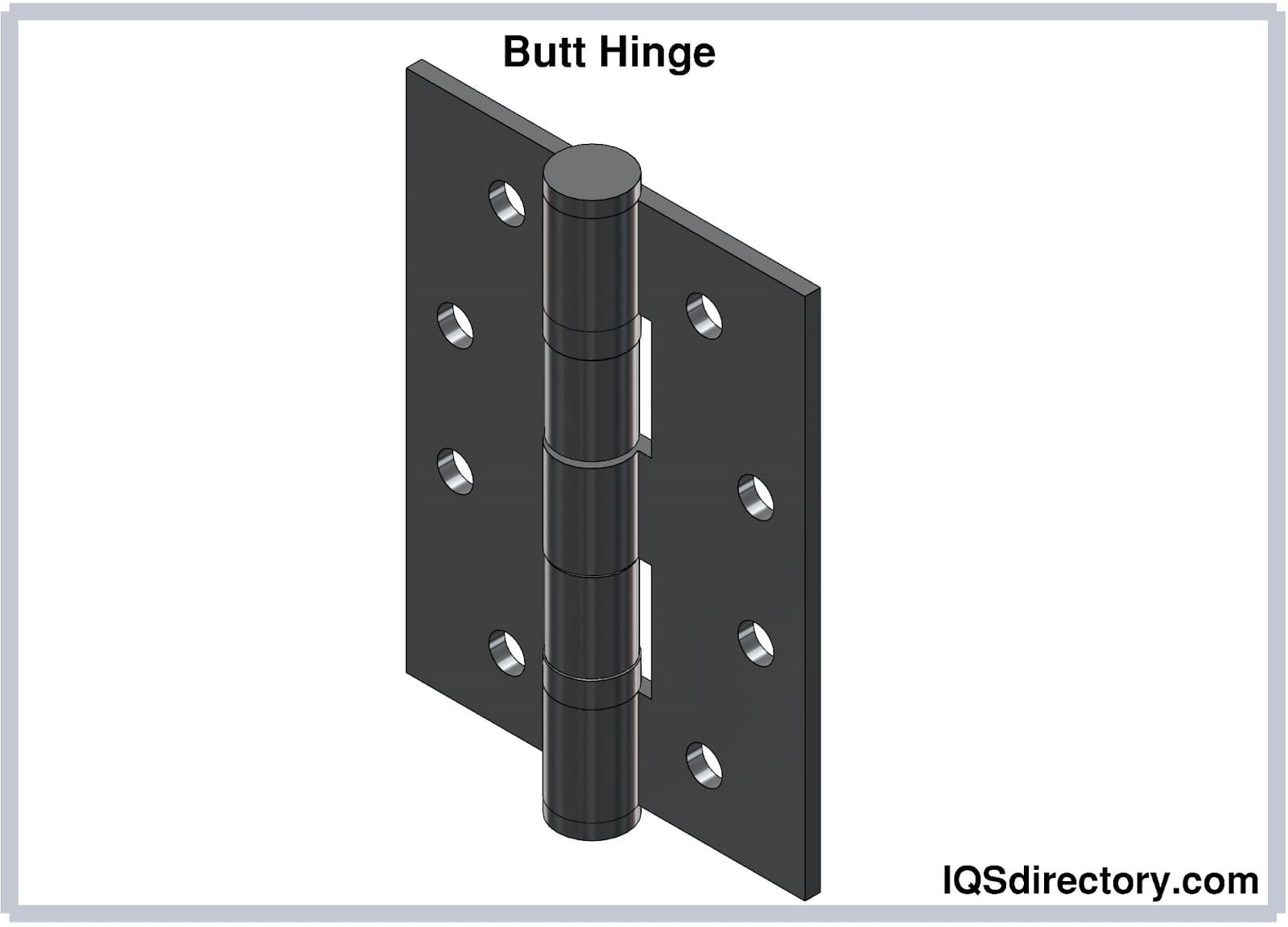
Butt Hinge
Butt hinges are the simplest hinge type, and consist of two leaves, aligned knuckles and a pin. Most often, they’re used as door hinges, though they cannot always be applied directly to a door or a door frame. When this is the case, manufacturers make an accompanying recession in the shape of a hinge, known as a mortise, into the door or the door frame. They can also be used as gate hinges/gate latch hinges.
Continuous Hinge
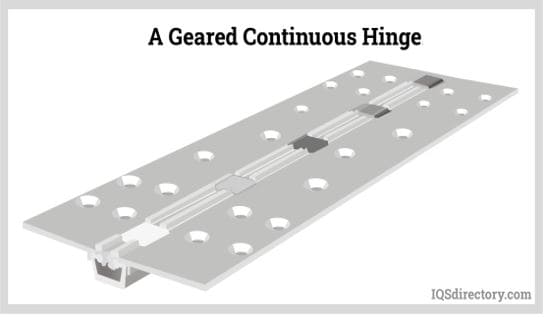
Continuous hinges are similar to butt hinges, but are extended, and are often found between joints in small containers such as tool boxes, and larger items such as piano panels. Note that continuous hinges, especially the type that can be found in containers, can be made with hinge springs.
Strap Hinge
Another type of hinge, strap hinges, are defined by their length. Strap hinges are frequently used for doors. Some varieties of strap hinges are made to extend across a door’s entire width.
Pivot Hinge
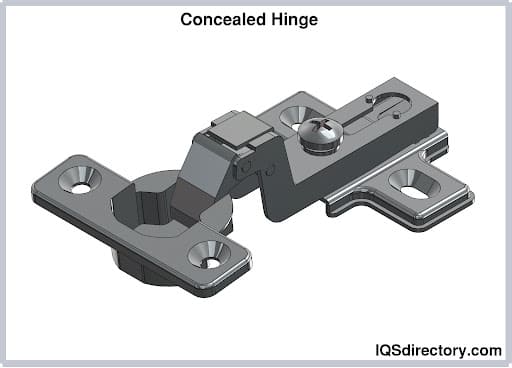
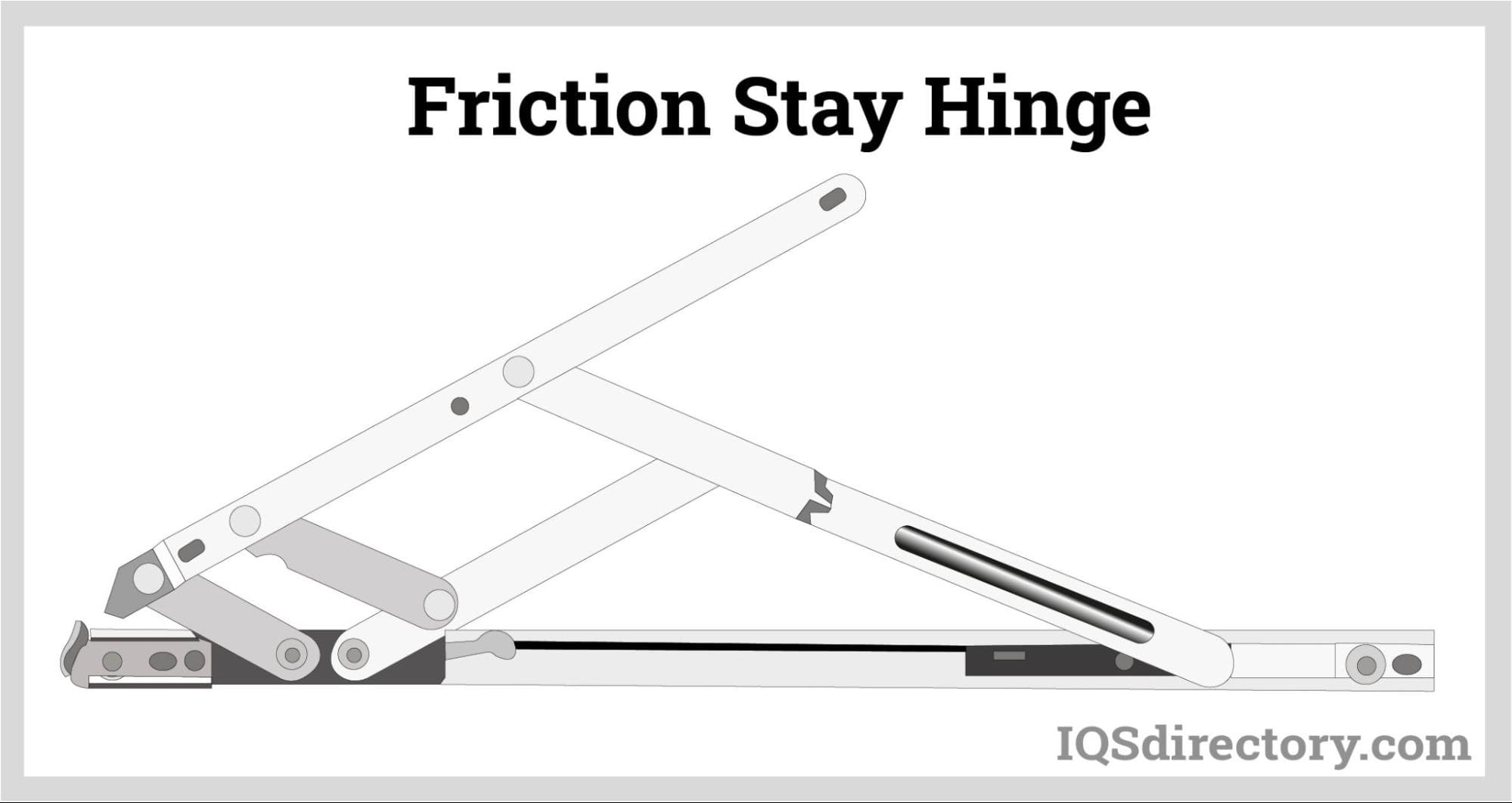
Pivot hinges rotate, or pivot, around a single point rather than a pin. They come in many different varieties, including the knife hinge, j-bolt pivot hinge, barrel hinge and conceal hinge/invisible hinge. Pivot hinges are usually used as door hinges for high traffic or extra heavy doors. They work well for this because, installed at both the top of the door frame and the floor, they can handle a lot of weight and reduce stress on the frame.
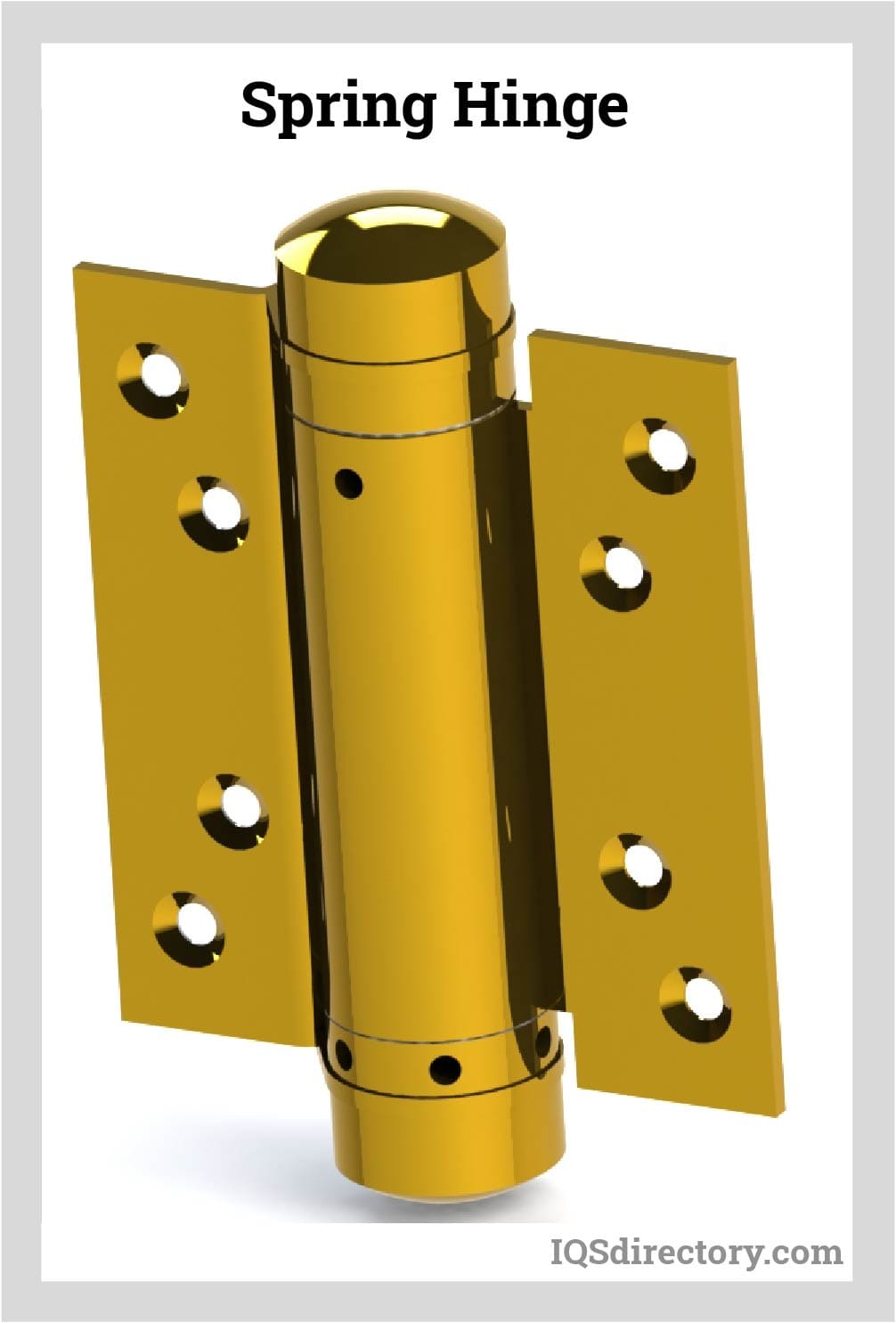
Spring Hinge
Spring hinges, or spring load hinges, can have a simple or complex design. The most simplistic variety of spring hinge is essentially a butt hinge with a coil tightly wound around its pin. The coil is prone to unwind, which forces the hinge’s leaves toward or away from each other. More complex designs can feature multiple coils as well as concealed coils. Regardless of their complexity, spring hinges are designed to either hinder or increase motion between two joined planes.
Weld-On Hinge
Weld-on hinges are commonly used for suspending heavy doors. The more heavy-duty variety of weld-on hinges are capable of holding door weights anywhere from several hundred pounds up to 10 tons. These heavy-duty hinges can be found in applications such as bank vaults and blast doors. The lighter variety of weld-on hinges can be found in applications such as wrought-iron gates. There are some applications where lightweight weld-on hinges can be painted in order to achieve a certain aesthetic appeal.
Heavy Duty Hinge
Heavy duty hinges can be welded on, and are primarily defined by their capacity to bear large loads. These hinges can be used for a variety of applications and are composed of a wide range of materials, from the lightweight aluminum to the stronger and more rust-resistant stainless steel.
Slip Joint Hinge
Also known as a slip hinge, a loose joint hinge or a take-apart hinge, a slip joint hinge is used with removable lid and door applications. It is used for livestock gates, lighting control panels, fire truck compartments, refuse containers and more. Slip joint hinges are popular for such applications because they allow a panel or door to be completely removed from its frame. In other words, they offer easy access to contents.
Flag Hinge
Flag hinges are distinct for their ability to swivel 360° around a fixed pin. In addition, they can be taken apart with said fixed pin on one leaf.
Power Hinge
A power hinge, also known as an electric power transfer hinge, is a hinge that features electrical components. They are quiet, heavy duty and easily concealed. It offers electronic locking access control and excellent security.
Friction Hinge
Friction hinges are capable of both creating resistance and allowing for a fluid range of motion. Friction hinges are used for container covers, doors, and an assortment of other planar items, and can either hinder or enable movement when desired. Over the years, the demand for highly functional hinges has risen since portable electronics have become less expensive; therefore, developmental advances in frictional hinges have been made.
Advantages of Hinges
Hinges may compete with alternative mechanisms or materials that serve similar purposes in various applications. One such competitor is sliding mechanisms, which are often used in place of hinges for doors, windows, and cabinets. While sliding mechanisms have their advantages in space-saving and smooth motion, hinges offer better stability and durability. Hinges are less prone to jamming or misalignment, making them more reliable for long-term use. Additionally, hinges allow doors and windows to swing open fully, providing better access and ventilation, which may be limited with sliding mechanisms.
In certain scenarios, magnets might be considered as an alternative to hinges. Magnets offer a seamless and silent closure in applications like jewelry and locket clasps. However, hinges are often preferred for jewelry and lockets as they provide a more distinct and secure closing mechanism. Hinges also allow for more intricate designs and flexibility in the range of motion, enhancing the overall aesthetic and functionality of the jewelry piece.
For foldable furniture and structures, hinges could face competition from flexible or articulated joints. While flexible joints can offer adjustable angles, they may lack the structural stability and firmness that hinges provide. Hinges ensure a defined and repeatable range of motion, allowing for reliable folding and unfolding of items like tables or folding walls. Moreover, hinges can be engineered to support heavy loads, making them more suitable for robust furniture construction.
In some situations, ropes, cords, or straps may be used instead of hinges to create flexible connections. For gates or doors, however, ropes or cords may not provide the same level of security or controlled motion as hinges. Hinges enable precise alignment and controlled swinging, which are essential for secure and reliable access points in fences and gates.
While hinges can be more complex and costly to manufacture than some alternatives, their reliability, smooth operation, and versatility make them a superior choice for many applications. The precise engineering of hinges allows them to withstand repeated use, varying loads, and environmental conditions, ensuring long-lasting performance and safety. Overall, hinges excel in providing a balance of structural integrity, smooth motion, and adjustability, making them the preferred choice in a wide range of scenarios where alternative mechanisms might fall short.
Accessories
Various accessories are available to enhance the functionality and usability of hinges in different applications. One essential accessory is the tip-on touch latch, which enables doors and cabinets to open with a gentle push, without the need for handles or knobs. These latches are particularly useful in modern, handle-less designs, providing a clean and sleek appearance while maintaining easy access to the enclosed items. Tip-on touch latches are commonly used in kitchens, closets, and furniture where a streamlined aesthetic is desired.
Angle restriction clips are accessories that limit the swing angle of doors or gates. They are beneficial in situations where a door should not open fully, preventing it from hitting adjacent structures or walls. These clips find application in tight spaces or areas with limited clearance, ensuring safe and controlled door operation.
Doorstops are accessories designed to prevent doors from opening too wide or banging against walls or furniture. They protect both the door and surrounding structures from damage. Doorstops come in various forms, such as wall-mounted or floor-mounted types, providing flexibility in choosing the most appropriate option based on the door’s specific requirements and the available space.
Compact adaptors are accessories used in conjunction with hinges to enable soft-closing functionality. When attached to the hinge, the compact adaptor controls the closing speed of the door or cabinet, preventing it from slamming shut and reducing wear on both the hinge and the door itself. Soft-closing hinges are popular in household applications where noise reduction and gentle handling of doors and cabinets are desired.
Stainless steel hinge eye bolts are accessories commonly employed in marine or outdoor applications. These durable and corrosion-resistant eye bolts are used to attach hinges to doors, gates, or panels in harsh environments, where standard materials might succumb to rust and degradation over time.
Door cushions, also known as door bumpers or buffers, are accessories that dampen the impact of a closing door, providing a cushioned and silent closing experience. These accessories are particularly useful in quiet environments, such as bedrooms or libraries, where loud door slamming is undesirable.
Determining the need for these accessories depends on the specific requirements and preferences of the application. For instance, in modern and minimalist designs, tip-on touch latches may be preferred to maintain a clean and handle-less appearance. In scenarios where space is limited or specific door angles are required, angle restriction
clips become valuable accessories. Soft-closing hinges with compact adaptors are beneficial for those seeking a smooth and quiet door-closing experience, particularly in high-traffic areas. Stainless steel hinge eye bolts are essential in marine or outdoor environments where corrosion resistance is crucial. And finally, door cushions are useful for anyone who wishes to reduce noise and protect doors and walls from damage.
In summary, these hinge accessories cater to various needs, from aesthetics to functionality and durability. Choosing the right accessory depends on the specific application and desired features, ultimately improving the performance and user experience of hinges in their respective roles.
Installation
While the details vary from hinge to hinge, their basic installation method is pretty straightforward. Start by marking the hinge’s location on the door or frame and pre-drilling pilot holes to prevent splitting. Then, attach the hinge to the door or frame with screws, ensuring it is flush and secure. Next, check the alignment by opening and closing the door and make any adjustments if needed. For heavier doors, install multiple hinges evenly spaced. Fine-tune the door’s position with hinge screw adjustments if necessary. Add accessories like tip-on touch latches or soft-closing mechanisms as desired and thoroughly test the door to ensure smooth operation. Finally, refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific instructions and follow best practices to ensure a successful and durable hinge installation.
Proper Care for Hinges
We’re happy to report that hinges are quite easy to maintain, whether they are residential hinges or industrial hinges.
To remove dust, dirt or grime from any hinge, you need only wipe it with a damp cloth, wetted with water. If the screw holes of your hinges begin to sag or become damaged, consider re-attaching them with carpenter glue. Note: This tip only applies to low-stakes hinges. While you may be able to re-attach screw holes to your industrial hinges this way, it’s best to double check with your manufacturer to make sure this provides a strong and safe enough bond for your purposes.
Speaking of industrial hinges, if you’d like to help your hinge survive in a harsh or heavy-use environment, we suggest you regularly lubricate them with an approved lubricant. Do so by removing the pin, applying the lubricant to it directly and then re-inserting it into the knuckle. This will help them fight damages like abrasion and corrosion.
Standards
The creation and use of hinges are subject to various standards set by national and international organizations to ensure safety, performance, and quality. One of the prominent standards for hinges is established by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). ANSI standards, such as ANSI/BHMA standards for hinges, outline the requirements for hinge materials, load-bearing capacities, endurance testing, and other performance criteria. Additionally, organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) also set global standards for hinges, aiming for international consistency and interoperability.
Consequences of hinges not meeting these standards can be significant for both manufacturers and users. For manufacturers, failure to comply with standards may result in liability issues, product recalls, or legal penalties if hinges cause accidents or injuries due to subpar performance. It can also damage the company’s reputation and lead to decreased customer trust and market share. For users, hinges that do not meet standards may pose safety risks, compromising the structural integrity of doors, cabinets, or other components. Users might experience frequent failures, reduced durability, or difficulty in installation, leading to additional maintenance costs and potential accidents.
On the other hand, there are considerable benefits for both manufacturers and users when producing or using hinges that meet these standards. For manufacturers, adhering to established standards demonstrates a commitment to quality, safety, and customer satisfaction. Compliance enhances product reliability, reduces liability risks, and boosts the company’s reputation in the industry. Meeting standards also fosters international trade by ensuring that hinges can be used in various applications worldwide.
For users, using hinges that meet standards provides assurance of safety and reliability. It ensures that the hinges will perform as expected, supporting the smooth operation of doors, cabinets, or other components. Meeting standards also facilitates interchangeability, allowing users to replace or upgrade hinges without compatibility concerns. Moreover, hinges meeting recognized standards are more likely to undergo rigorous testing and quality checks, leading to increased longevity and reduced maintenance costs for end-users.
In summary, standards set by organizations like ANSI and ISO play a critical role in ensuring the quality and safety of hinges. Non-compliance can have serious consequences for both manufacturers and users, including legal issues, safety hazards, and reputational damage. Conversely, adhering to standards provides numerous benefits, including enhanced reliability, international compatibility, and improved overall user satisfaction, making it essential for manufacturers and users to prioritize hinges that meet established industry standards.
Things to Consider
When considering a hinge purchase, you need to think about your application requirements, i.e.: your desired aesthetics, dimensions and weight of objects to which hinges will be attached, projected frequency of use, application setting/environment (sea salt exposure, humidity levels, etc.) and industry requirements and regulations.
To get the very best match, you need to take your design specifications to a manufacturer or supplier that is not only experienced and reliable, but also a good fit for you. To help you find that high quality fit, we’ve compiled a comprehensive listing of manufacturers and suppliers we trust. Learn more about each of them by studying their respective profiles, which you find in the middle of this page. As you browse, take note of three or four companies in whom you’re most interested, then reach out to each of them individually. Discuss not only your special hinge specifications, but also your budget and timeline. Your goal is to find a hinge company that wants to do everything they can to create a hinge that meets all of your specifications and requests, while working within your budget. In short, you want to choose a manufacturer that works from a customer-centric viewpoint. We believe the right company is one of those on this page. Once you’ve found them, contact them to get started.




 Bolts
Bolts Fasteners
Fasteners Gas Spring
Gas Spring Handles
Handles Hinges
Hinges Latches
Latches Locks
Locks WIre Hooks
WIre Hooks Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services