Hinges are mechanical bearings used to join together two objects. They allow these objects to move on a limited angle of rotation relative to one another without falling apart. Read More…
We take our customer evaluations as our only measure of success. If our customers are not happy, we are not happy! We will work with you until we find the right hinges solution for you.

Brookfield Industries is a manufacturer of high-capacity door hinges and pivots. We also manufacture special application door operators with a full-line of detention grade and industrial stainless steel hinges with capacities ranging from 300 lbs to 50 tons. We offer seven categories of hinges, and within those categories we offer several subcategories – we can meet your company’s hinge needs.

We are here to provide you with any hinge you could ever possibly need! We are the hinge specialists committed to bringing you a level of customer service that is unmatched by the competition.

Hardware Mfg. supplies stock inventory parts in addition to creating custom components for OEM and resellers. We work with a number of different industries such as agriculture, drug tablet, livestock, truck equipment, conveyors, and more.

Specializing in custom-made hinges is what Hinge & Hardware is known for. We also stock certain types of standard models to round out the availability for our customers. The aforementioned are available as mild steel, aluminum and stainless. We also have a wider hardware line that includes door seals, gaskets, handles, a variety of latches and enclosure hardware.

More Hinge Manufacturers
Applications
Hinges are indispensable components in numerous industries, providing pivotal support and functionality. In the realms of building and furniture construction, they find extensive use in cabinets, doors, windows, and tables. Cabinet hinges ensure the seamless opening and closing of doors, while door hinges allow for effortless swinging. Window hinges not only enable smooth operation but also secure locking, which enhances energy efficiency. In furniture design, hinges play a crucial role in creating foldable and adjustable pieces, thereby boosting versatility and practicality.
In the aerospace industry, hinges play a crucial role in aircraft components such as flaps, ailerons, and landing gear doors. These aviation hinges ensure precise control of moving parts, enhancing the safety and efficiency of aircraft in flight. Similarly, in marine applications, hinges are indispensable for doors, hatches, and access panels, providing dependable and secure movement in the challenging marine environment. In the military and defense sectors, hinges are equally vital for vehicle components like hatches, doors, and access panels. They offer robustness and reliability under extreme conditions, ensuring smooth functionality and rapid access when necessary.
Turning our attention to the world of jewelry and lockets, delicate hinges play a crucial role in crafting exquisite and ornamental lockets. These tiny mechanisms not only enhance the visual charm of these pieces but also allow them to open gracefully, revealing hidden treasures or cherished photographs within. Similarly, in the realm of musical instruments, pianos are deeply reliant on hinges for their intricate action mechanisms. These hinges enable the hammers to strike the strings with precision, producing a symphony of diverse tones and harmonies.
Hinges play a vital role in both cages and fences, where they are essential for gates and doors. These structures rely on heavy-duty hinges to bear their weight, allowing for smooth opening and closing, which ensures both security and convenient access. In contrast, home appliances and electronics use hinges in their foldable and adjustable components. Laptops and smartphones, for example, depend on hinges to open and close their screens, providing the necessary flexibility and portability for everyday use.
In material handling and storage, hinges play a crucial role in storage lockers, toolboxes, and industrial cabinets. These hinges withstand constant use, ensuring secure closure and contributing significantly to the organization and protection of items. In the automotive industry, hinges are indispensable for car doors, hoods, trunks, and foldable seats. Subjected to rigorous testing, these hinges are designed to provide enduring performance and ensure passenger safety.
For barrier and fencing applications, hinges are essential for gates and access points. They enable gates to swing open and closed, ensuring controlled entry and exit for both pedestrians and vehicles. In architecture, hinges play a crucial role in various movable elements such as large pivoting doors, foldable walls, and adjustable louvers. These innovative hinge applications create dynamic and adaptable spaces, enhancing both the functionality and aesthetics of modern buildings.
Hinges are vital and versatile components found in countless applications across various industries. Their ability to offer smooth movement, adjustability, and structural integrity makes them indispensable in the design of cabinets, doors, windows, gates, lockers, tables, airplanes, marine and military vehicles, jewelry, pianos, cages, fences, home appliances, electronics, and beyond. From aerospace to architecture, hinges are crucial in enhancing numerous aspects of our daily lives and industrial operations.
The History of Hinges
Hinges are among humanity’s most enduring companions, their precise origins lost to the mists of time. We do know, however, that they’ve been in use in the Middle East since at least the Bronze Age. Some of the oldest hinge artifacts, unearthed in Turkey at the site of Hattusa, the ancient capital of the Hittite Empire, date back to around 1600 BC. These early hinges were likely reserved for significant and sacred structures. This pattern of use is echoed across ancient civilizations; for instance, the Old Testament mentions hinges only in reference to King Solomon’s temple. Similarly, hinges discovered in the ruins of ancient Assyrian and Babylonian cities have been found solely in temples, not in ordinary homes, likely due to the high cost of production.
As the Middle Ages unfolded, blacksmithing flourished, and metal became more affordable. Consequently, ordinary people began to use hinges on their doors. The application of hinges soon broadened, finding their way onto gates, wagons, ships, jewelry boxes, and lock boxes.
Fast forward a few centuries to the dawn of the Industrial Revolution, a period that saw a significant leap in hinge production and innovation. This era’s burgeoning machinery relied heavily on hinges, which, thanks to advanced manufacturing techniques, could now be made with greater complexity, precision, and efficiency. Among the notable inventions of the time was the ball bearing hinge, designed for smoother operation. In 1899, Stanley’s Bolt Manufactory, the precursor to StanleyWorks, secured a patent for this innovative hinge design.
The 20th and 21st centuries have ushered in a wave of innovations in hinge manufacturing. These advancements include a broader selection of materials, the application of protective coatings, the creation of intricate designs, and accelerated production processes. Moreover, contemporary hinges enhance the range of motion for the objects they support.
Design
Production Process
Hinge and latch manufacturers kick off their production by heating the metal they’ll work with. Once it reaches the right temperature, they subject it to various machining processes, such as deformation, extrusion, casting, or cutting. The choice of machining method depends on factors like budget, required production volume, desired speed, and the complexity of the design.
After machining the hinge, manufacturers typically subject it to one or more additional processes. These steps are aimed at refining the piece, involving procedures like plating, painting, coating, polishing, rust-proofing, galvanization, or smoothing. The decision to utilize these secondary processes hinges on the anticipated exposure to potential damage such as corrosion, wear, or abrasion.
Materials
Manufacturers typically craft hinges using either hollow or solid metal materials. These may include steel, stainless steel, chrome, copper, nickel, solid brass, and bronze, each offering distinct qualities such as durability, tensile strength, corrosion resistance, ductility, temperature tolerance, and aesthetic appeal. For instance, brass hinges are favored for their decorative value due to their appealing color. In some cases, manufacturers opt for plastic materials to create hinges that are economical, resistant to heat, rust, chemicals, and UV rays, and require no lubrication.
Considerations and Customization
When designing hinges, manufacturers typically begin with three fundamental components: the leaves, the knuckle, and the hinge pin. The leaves serve as extended plates that are interconnected through the knuckle, acting as a hollow joint. The knuckle, in turn, is secured by the hinge pin. During installation, users attach the leaves to their desired surfaces and drill a hole in each leaf to fasten them securely together.
Manufacturers wield substantial creative freedom in varying several aspects: hinge length (measured parallel and from leaf edge to edge), knuckle length (along each knuckle parallel to the pin), leaf gauge (thickness in mm), width (from pin center to leaf edge), slope (angular movement of leaves), pitch (knuckle edge distance on the same leaf), and end play (axial leaf movement). They can intentionally design gaps between knuckles and leaves to enhance hinge motion and fluidity.
Manufacturers offer extensive customization options for hinges. They can tailor the size to almost any specification you need. Moreover, they can enhance the aesthetics by incorporating complementary colors or matching finishes, adding a touch of shine. For those preferring discreet installations, manufacturers can design hinges to be entirely concealed, ensuring they blend seamlessly into the background.
Types
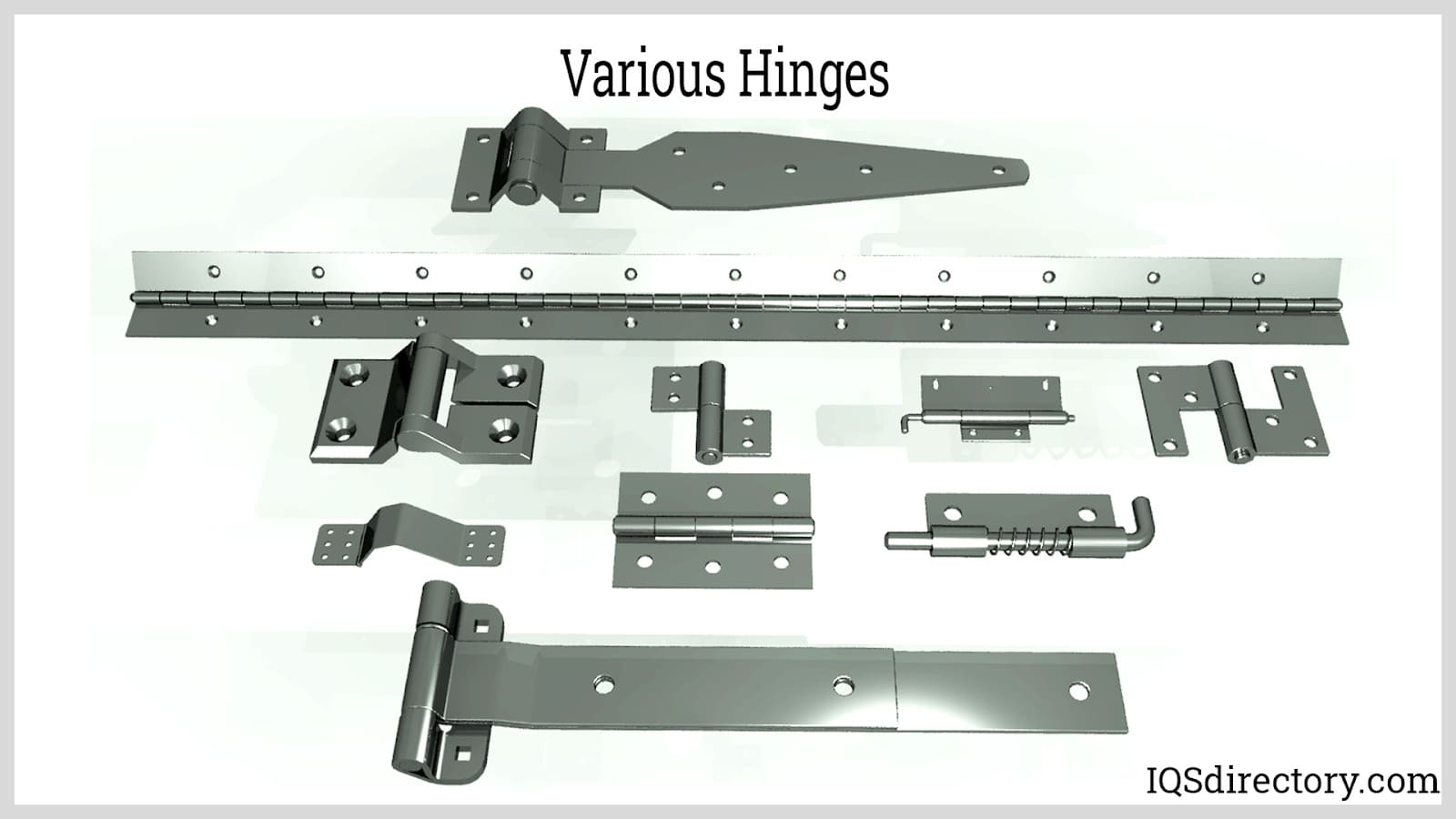
Hinges come in a vast array of compositions and configurations, reflecting their widespread use across numerous industries. Among the simplest types are butt hinges and continuous hinges, often referred to as piano hinges.
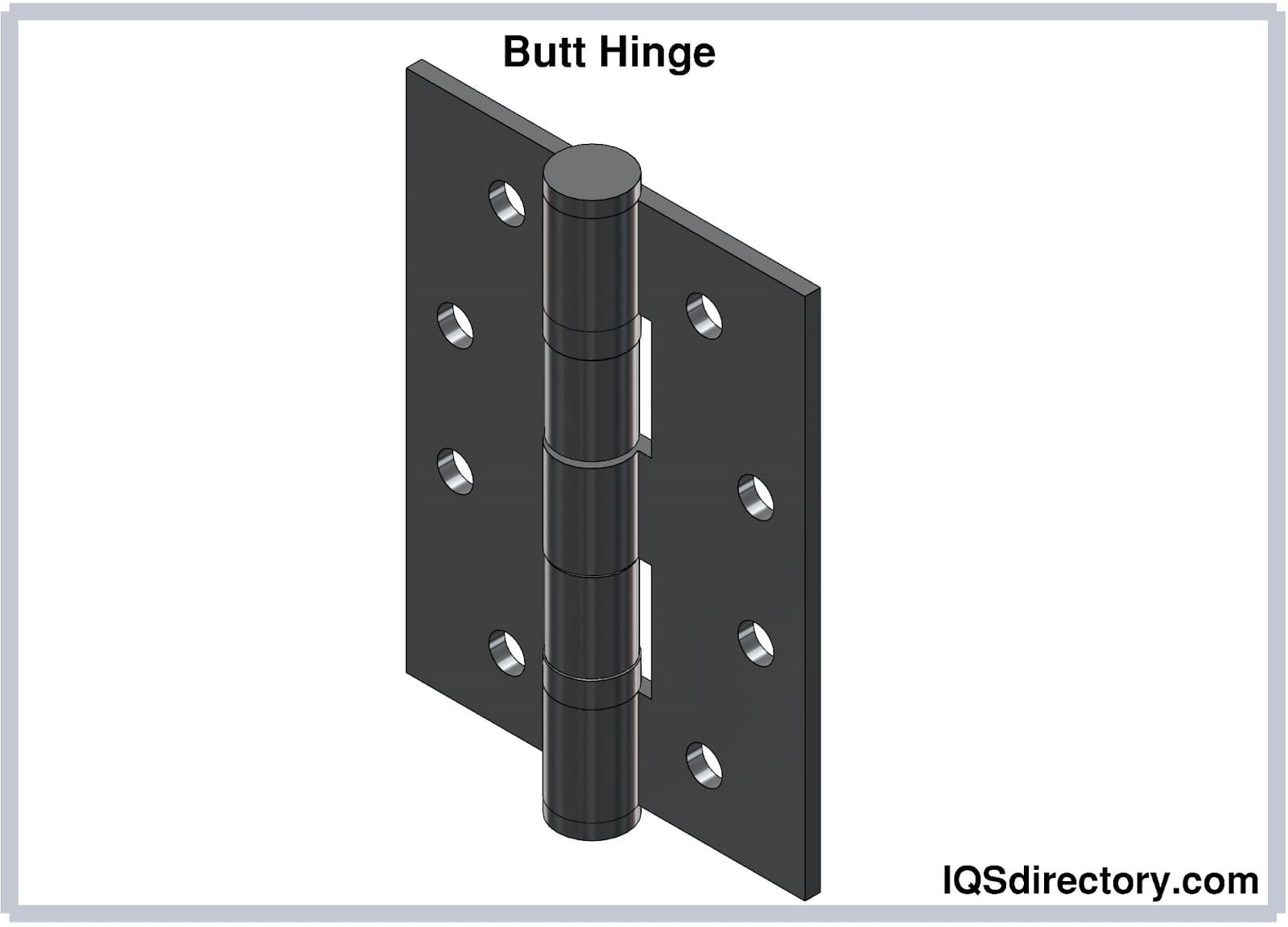
Butt Hinge
Butt hinges, the most basic hinge type, consist of two leaves with aligned knuckles connected by a pin. Primarily used for doors, they require a mortise—a recess cut into the door or frame—to function properly when not directly applicable. They also find utility as gate hinges or gate latch hinges.
Continuous Hinge
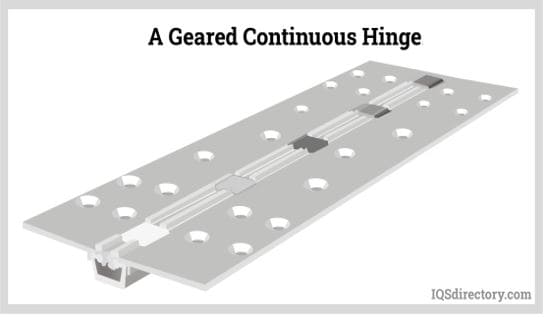
Continuous hinges, resembling butt hinges but extended, commonly link joints in small containers like toolboxes and larger items such as piano panels. It’s important to note that continuous hinges, particularly those used in containers, may feature hinge springs.
Strap Hinge
Strap hinges, another variety of hinge, are distinguished by their length. They are commonly employed for doors, with certain types designed to span the entire width of a door.
Pivot Hinge
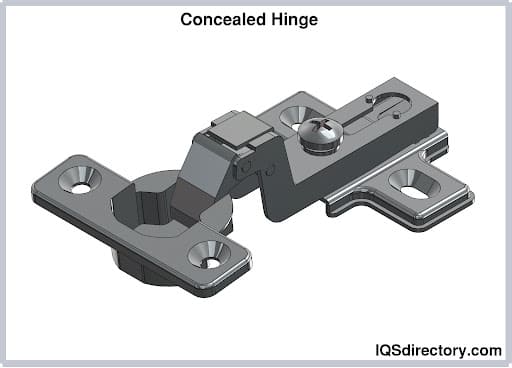
Pivot hinges revolve around a central point rather than a typical pin. They span a variety of types, such as knife hinges, j-bolt pivot hinges, barrel hinges, and concealed/invisible hinges. These hinges are commonly employed on doors subjected to high traffic or those with substantial weight. Positioned at both the top of the door frame and the floor, they effectively distribute weight and minimize strain on the frame.
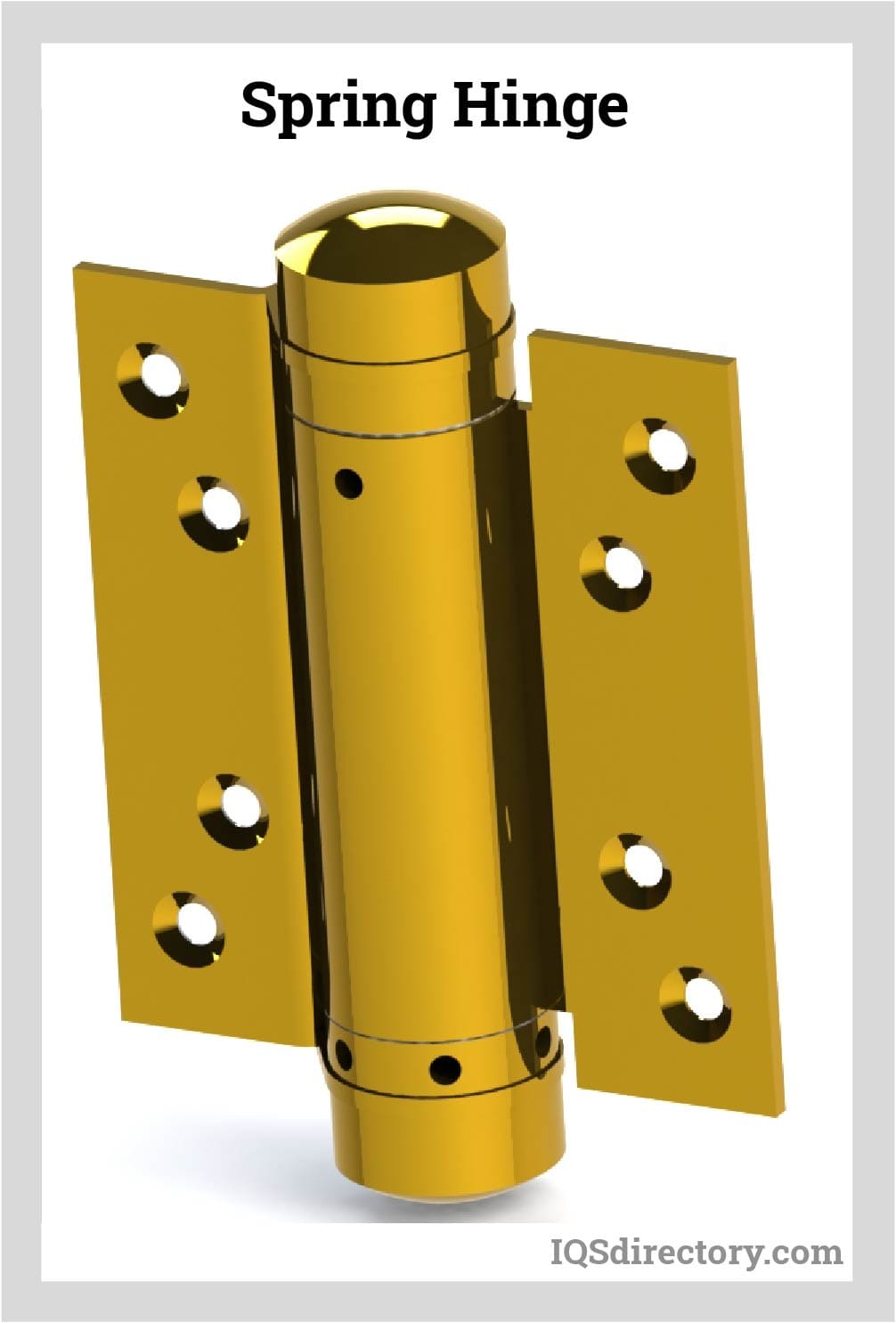
Spring Hinge
Spring hinges, also known as spring-loaded hinges, come in varying degrees of complexity. At their simplest, these hinges resemble butt hinges with a tightly wound coil around the pin. This coil, prone to unwinding, pushes the hinge’s leaves either together or apart. More intricate designs may incorporate multiple coils, sometimes concealed, enhancing their functionality. Whether straightforward or intricate, spring hinges serve to regulate or amplify movement between connected surfaces.
Weld-On Hinge
Weld-on hinges serve as stalwart suspensions for hefty doors, with heavy-duty types bearing the brunt of weights ranging from several hundred pounds to a colossal 10 tons. They fortify applications like bank vaults and blast doors. Conversely, lighter variants grace wrought-iron gates, offering a durable pivot. In select settings, these lightweight weld-on hinges are even painted to enhance their visual allure, blending function with aesthetic finesse.
Heavy Duty Hinge
Heavy duty hinges, capable of bearing substantial loads, can be securely welded into place. They find versatile application across various uses, crafted from materials spanning lightweight aluminum to robust, rust-resistant stainless steel.
Slip Joint Hinge
A slip joint hinge, also referred to as a loose joint hinge, a slip hinge, or a take-apart hinge, finds its application in various settings requiring removable lids and doors. Commonly used in livestock gates, lighting control panels, fire truck compartments, refuse containers, and similar applications, slip joint hinges enable easy removal of panels or doors from their frames. This feature facilitates convenient access to the contents enclosed within.
Flag Hinge
Flag hinges stand out due to their unique capability to rotate a full 360° around a fixed pin. Moreover, they can effortlessly be disassembled using this fixed pin located on one leaf.
Power Hinge
A power hinge, alternatively termed an electric power transfer hinge, integrates electrical components. It operates quietly, withstands heavy-duty use, and can be discreetly concealed. This hinge facilitates electronic access control through locking mechanisms, ensuring robust security.
Friction Hinge
Friction hinges serve dual roles by providing resistance while facilitating a smooth range of motion. They find applications in container lids, doors, and various flat surfaces, balancing the ability to restrict or enable movement as needed. With the decreasing cost of portable electronics over the years, there has been a growing demand for highly functional hinges. Consequently, significant strides have been made in the development of friction hinges to meet these evolving needs.
Advantages of Hinges
Hinges often compete with sliding mechanisms, which are used in similar applications like doors, windows, and cabinets. Although sliding mechanisms can save space and offer smooth movement, hinges provide superior stability and durability. They are less likely to jam or become misaligned, making them more reliable for long-term use. Additionally, hinges allow doors and windows to fully open, enhancing access and ventilation, which sliding mechanisms may restrict.
In some cases, magnets can be used instead of hinges. Magnets provide a smooth and quiet way to close items such as jewelry clasps and lockets. However, hinges are usually chosen for these applications because they offer a more secure closure. Additionally, hinges allow for more complex designs and a wider range of motion, improving both the look and function of the jewelry.
In the realm of foldable furniture and structures, hinges might soon be challenged by flexible or articulated joints. Although these joints allow for adjustable angles, they often do not provide the same level of structural stability and firmness as hinges. Hinges offer a consistent and precise range of motion, which is essential for the dependable operation of foldable items such as tables or walls. Hinges are designed to handle heavy loads, making them a better choice for sturdy furniture construction.
In certain cases, ropes, cords, or straps can replace hinges to allow for flexibility. However, for gates or doors, these materials might not offer the same security or controlled movement as hinges do. Hinges provide accurate alignment and steady swinging, crucial for secure and dependable openings in fences and gates.
While hinges may demand greater complexity and expense in their creation compared to other options, their dependable performance, seamless functionality, and adaptability render them a standout selection for numerous uses. Engineered with precision, hinges excel in enduring the rigors of frequent usage, diverse loads, and challenging environmental conditions, guaranteeing sustained efficacy and safety. Hinges masterfully blend strength, fluid movement, and versatility, emerging as the top choice in numerous situations where other mechanisms simply can’t measure up.
Accessories
A range of accessories can elevate the versatility and performance of hinges across multiple settings. A standout among these is the tip-on touch latch, designed to allow doors and cabinets to swing open with a simple nudge, eliminating the need for handles or knobs. This feature shines in contemporary, handle-free designs, offering a minimalist and smooth facade while ensuring contents are easily accessible. Tip-on touch latches find their niche in environments like kitchens, closets, and furniture pieces that favor a sleek, uncluttered look.
Angle restriction clips are used to limit how far doors or gates can open. They prevent doors from swinging fully open and hitting nearby walls or structures. These clips are useful in small spaces or areas with limited room, helping to ensure that doors open safely and only as far as needed.
Doorstops are used to keep doors from opening too wide or hitting walls or furniture. They help prevent damage to both the door and nearby structures. Available in different styles like wall-mounted or floor-mounted, doorstops offer various options to suit the door’s needs and the space available.
Compact adapters are accessories that work with hinges to allow doors or cabinets to close softly. By controlling the speed at which the door closes, these adapters prevent it from slamming, thereby reducing noise and wear on both the hinge and the door. They are commonly used in homes to ensure doors and cabinets close quietly and smoothly.
Stainless steel hinge eye bolts are essential fixtures frequently utilized in marine or outdoor settings. Their robust and rust-resistant nature makes them ideal for securing hinges to doors, gates, or panels in environments where ordinary materials may fall prey to corrosion and wear.
Door cushions, often referred to as door bumpers or buffers, serve as gentle guardians against the harsh clatter of closing doors. They soften the door’s impact, ensuring a quiet and smooth closure. These handy accessories are especially valuable in tranquil spaces like bedrooms or libraries, where the abrupt sound of a door slamming would be unwelcome.
Deciding whether to use these accessories hinges on the specific demands and tastes of the application. For example, in sleek and minimalist designs, tip-on touch latches are often chosen to preserve a streamlined, handle-free look. In situations where space is at a premium or certain door angles are necessary, angle restriction clips prove to be essential tools. Soft-closing hinges fitted with compact adaptors offer a serene and seamless door-closing journey, ideal for bustling spaces. For settings exposed to the elements, like marine environments, stainless steel hinge eye bolts are indispensable due to their robust resistance to corrosion. Meanwhile, door cushions provide a dual benefit: muffling noise and shielding both doors and walls from wear and tear.
These hinge accessories are designed to meet a range of needs, spanning from visual appeal to practicality and longevity. Selecting the ideal accessory hinges on the specific use-case and the features sought, thereby enhancing both the efficacy and the overall experience of using hinges in their designated capacities.
Installation
Though the specifics might differ slightly from one hinge to another, the fundamental process of installing them is fairly direct. Begin by outlining where the hinge will sit on the door or frame and carefully pre-drill pilot holes to avoid any wood splitting. Secure the hinge in place using screws, making sure it’s perfectly flush and firmly attached. Then, test the door by opening and closing it to check the alignment, making adjustments as necessary to ensure a smooth swing. For bulkier doors, evenly distribute several hinges along the frame. Adjust the door’s alignment by tweaking the hinge screws if needed. Consider enhancing the door with optional features like tip-on touch latches or soft-closing mechanisms for added functionality. Thoroughly test the door to confirm its seamless movement. Always consult the manufacturer’s instructions for detailed guidance and adhere to recommended practices for a robust and lasting hinge installation.
Proper Care for Hinges
We’re pleased to share that maintaining hinges, from those in homes to the robust ones in industrial settings, is surprisingly simple.
To cleanse a hinge of dust, dirt, or grime, simply pass over it with a cloth moistened with water. Should the screw holes of your hinges show signs of sagging or wear, a dab of carpenter glue can often serve as a quick fix. However, this advice is best suited for non-critical hinges. For industrial-strength hinges, reattaching screw holes with just carpenter glue might not suffice. It’s prudent to consult with the manufacturer to ensure this method offers a robust and secure connection for your specific needs.
When navigating the rugged terrain of industrial settings, keeping your hinges in top condition is crucial. To shield your hinges from the relentless wear and tear of harsh environments, consider treating them to a regular dose of an approved lubricant. Start by liberating the pin from its housing, then anoint it generously with lubricant before reuniting it with the knuckle.
Standards
The design and application of hinges adhere to stringent guidelines established by both national and international bodies, which guarantee their safety, functionality, and excellence. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) sets a key benchmark for hinges, providing detailed guidelines like those found in ANSI/BHMA standards. These standards specify the essentials for hinge materials, their capacity to bear weight, endurance testing, and other vital performance measures. Moreover, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) crafts worldwide standards, striving for global uniformity and seamless interoperability in hinge design.
The repercussions of hinges failing to meet these standards can be substantial for both manufacturers and users. For manufacturers, non-compliance may lead to liability issues, product recalls, or legal penalties if substandard hinges cause accidents or injuries. Additionally, it can tarnish the company’s reputation, erode customer trust, and result in a decline in market share. When hinges fail to meet standards, they can jeopardize the safety and structural soundness of doors, cabinets, and other components. This can result in frequent breakdowns, diminished durability, and challenging installations for users. Consequently, this leads to higher maintenance expenses and an increased risk of accidents.
On the other hand, producing or using hinges that meet these standards has many benefits for both manufacturers and users. For manufacturers, following these standards shows a commitment to quality, safety, and customer satisfaction. It also improves product reliability, reduces liability risks, and enhances the company’s reputation in the industry. Additionally, meeting these standards supports international trade by making sure hinges can be used in various applications worldwide.
Using hinges that meet standards offers users safety and reliability. These hinges perform as expected, ensuring smooth operation of doors, cabinets, or other components. Standards also make it easier to replace or upgrade hinges without compatibility issues. Additionally, hinges that meet standards undergo rigorous testing and quality checks, which results in increased longevity and lower maintenance costs.
Organizations like ANSI and ISO set standards that are crucial for ensuring the quality and safety of hinges. If manufacturers do not comply with these standards, they can face serious problems, such as legal issues, safety risks, and damage to their reputation. On the other hand, following these standards offers many benefits, such as increased reliability, compatibility across countries, and better user satisfaction. Therefore, it is important for manufacturers and users to prioritize hinges that meet these industry standards.
Things to Consider
When buying a hinge, consider your specific needs. Think about the look you want, the size and weight of the objects you’ll attach the hinges to, how often you’ll use them, the environment they’ll be in (like exposure to sea salt or humidity), and any industry rules and regulations.
To secure the perfect match for your design needs, it’s essential to partner with a manufacturer or supplier that not only brings experience and reliability to the table but also aligns well with your specific requirements. We’ve curated a detailed directory of trusted manufacturers and suppliers. Delve into their profiles located mid-page to gather insights about each one. As you peruse, identify three or four companies that catch your interest, then reach out to them individually. Discuss your unique hinge specifications, budget, and timeline. Your aim is to find a company dedicated to crafting a hinge that fulfills all your criteria, all while staying within your budget. Essentially, you want a manufacturer that prioritizes customer satisfaction. We’re confident that the right partner is among the companies listed here. Once you’ve made your choice, contact them to begin your project.




 Bolts
Bolts Fasteners
Fasteners Gas Spring
Gas Spring Handles
Handles Hinges
Hinges Latches
Latches Locks
Locks WIre Hooks
WIre Hooks Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services